- start
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Remarks
- Examples
- start start
- Синтаксис Syntax
- Параметры Parameters
- Комментарии Remarks
- Примеры Examples
- 25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize
- How to open the Run dialog?
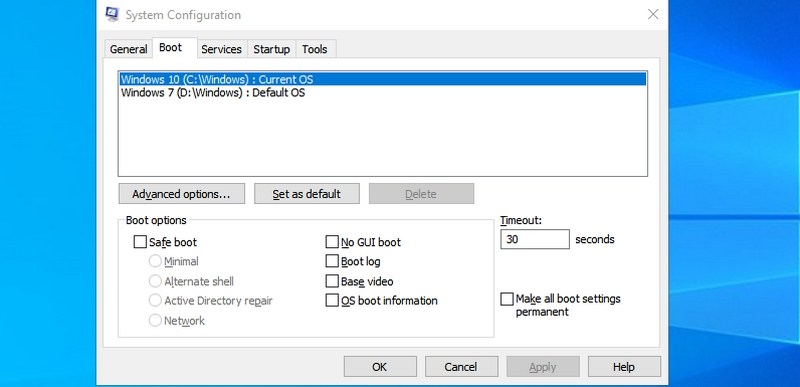
- #1. Access System Configuration — “msconfig”
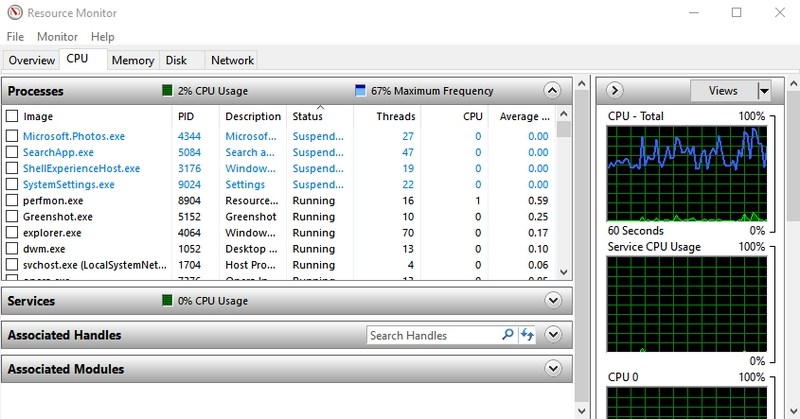
- #2. Access Resource Monitor — “resmon”
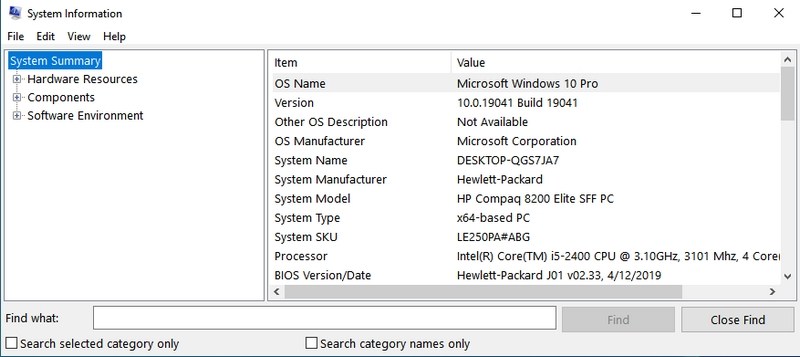
- #3. Open System Information — “msinfo32”
- #4. Access Backup and Restore window — “sdclt”
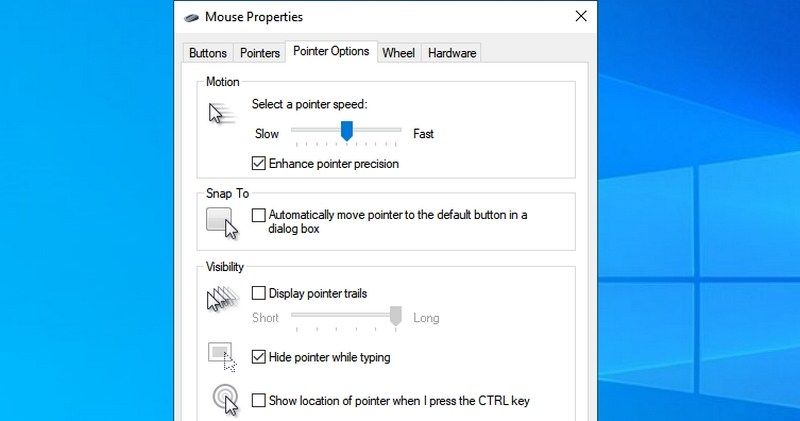
- #5. Access mouse properties — “main.cpl”
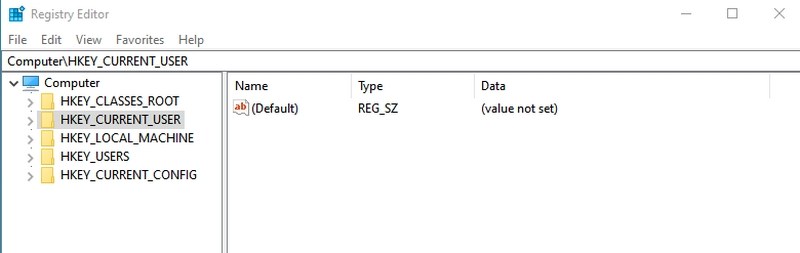
- #6. Open Windows Registry — “regedit”
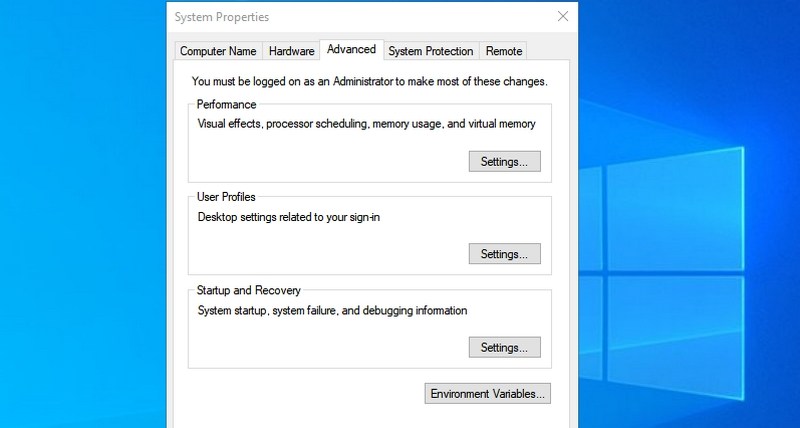
- #7. Access System Properties — “sysdm.cpl”
- #8. Manage Windows Power options — “powercfg.cpl”
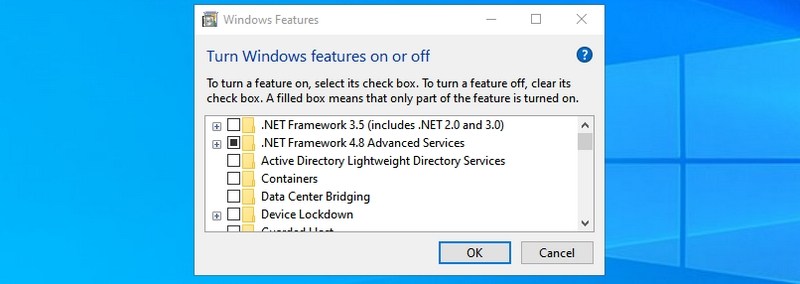
- #9. Open Windows Features — “optionalfeatures”
- #10. Open Magnifier — “magnify”
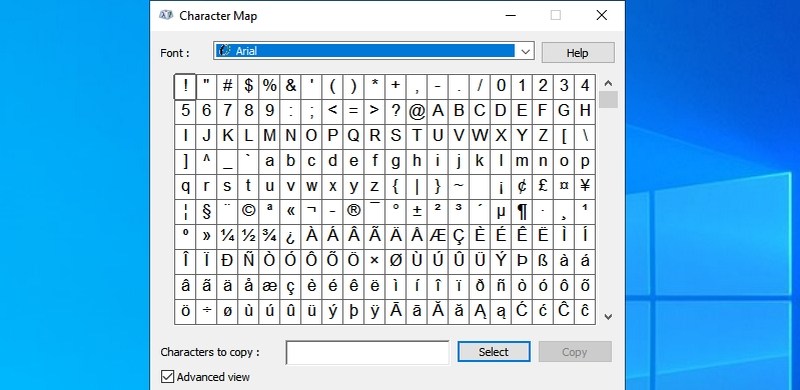
- #11. Open Character Map app — “charmap”
- #12. Access Network Connections — “ncpa.cpl”
- #13. Run Malicious Software Removal Tool — “mrt”
- #14. Open Device Manager — “devmgmt.msc”
- #15. Manage User Accounts — “netplwiz”
- #16. Open Services app — “services.msc”
- #17. Access Programs and Features window — “appwiz.cpl”
- #18. Open Control Panel — “control”
- #19. Open current user folder — “.” (period)
- #20. Open On-Screen Keyboard — “osk”
- #21. Open Snipping Tool — “snippingtool”
- #22. Open Windows Memory Diagnostic — “mdsched”
- #23. Open any website — “Insert website URL”
- #24. Open Remote Desktop Connection — “mstsc”
- #25. Open Command Prompt — “cmd”
- Wrapping up
start
Starts a separate Command Prompt window to run a specified program or command.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Specifies the title to display in the Command Prompt window title bar. | |
| /d |
. ]]
Remarks
You can run non-executable files through their file association by typing the name of the file as a command.
If you run a command that contains the string CMD as the first token without an extension or path qualifier, CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. This prevents users from picking up cmd from the current directory.
If you run a 32-bit graphical user interface (GUI) application, cmd does not wait for the application to quit before returning to the command prompt. This behavior does not occur if you run the application from a command script.
If you run a command that uses a first token that does not contain an extension, Cmd.exe uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. The default value for the PATHEXT variable is:
Note that the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons (;) separating each extension.
When searching for an executable file, if there is no match on any extension, start checks to see if the name matches a directory name. If it does, start opens Explorer.exe on that path.
Examples
To start the Myapp program at the command prompt and retain use of the current Command Prompt window, type:
To view the start command-line help topic in a separate maximized Command Prompt window, type:
start start
Запускает отдельное окно командной строки для запуска указанной программы или команды. Starts a separate Command Prompt window to run a specified program or command.
Синтаксис Syntax
Параметры Parameters
| Параметр Parameter | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| Задает заголовок, отображаемый в строке заголовка окна командной строки . Specifies the title to display in the Command Prompt window title bar. | |
| /d |
. ]]
Комментарии Remarks
Вы можете запускать неисполняемые файлы с помощью сопоставления файлов, вводя имя файла в виде команды. You can run non-executable files through their file association by typing the name of the file as a command.
При выполнении команды, содержащей строку CMD в качестве первого маркера без квалификатора расширения или пути, команда CMD заменяется значением переменной COMSPEC. If you run a command that contains the string CMD as the first token without an extension or path qualifier, CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. Это не позволяет пользователям выбирать cmd из текущего каталога. This prevents users from picking up cmd from the current directory.
Если вы запускаете приложение с 32-битным графическим пользовательским интерфейсом (GUI), программа cmd не ждет завершения работы приложения, прежде чем вернуться в командную строку. If you run a 32-bit graphical user interface (GUI) application, cmd does not wait for the application to quit before returning to the command prompt. Такое поведение не происходит при запуске приложения из командного скрипта. This behavior does not occur if you run the application from a command script.
При выполнении команды, использующей первый токен, который не содержит расширение, Cmd.exe использует значение переменной среды ПАСЕКСТ, чтобы определить, какие расширения следует искать и в каком порядке. If you run a command that uses a first token that does not contain an extension, Cmd.exe uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. Значение по умолчанию для переменной ПАСЕКСТ: The default value for the PATHEXT variable is:
Обратите внимание, что синтаксис аналогичен переменной PATH с точкой с запятой (;) Отделение каждого расширения. Note that the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons (;) separating each extension.
При поиске исполняемого файла, если нет совпадения с каким-либо расширением, запустите проверку, чтобы проверить, совпадает ли имя с именем каталога. When searching for an executable file, if there is no match on any extension, start checks to see if the name matches a directory name. Если это так, то Start открывает Explorer.exe по этому пути. If it does, start opens Explorer.exe on that path.
Примеры Examples
Чтобы запустить программу MyApp из командной строки и использовать текущее окно командной строки , введите: To start the Myapp program at the command prompt and retain use of the current Command Prompt window, type:
Чтобы просмотреть раздел справки по командной строке в отдельном окне командной строки с развернутым окном, введите: To view the start command-line help topic in a separate maximized Command Prompt window, type:
25 Run Commands in Windows You Should Memorize
Using Run commands in Windows is a very efficient way to access different Windows settings and apps directly.
If you memorize Run commands, you can access a particular app in just 2 steps instead of many clicks.
I personally don’t like frequently reaching out for the mouse; therefore, I have memorized all the required keyboard shortcuts and commands to minimize my interaction with the mouse. And Run commands are core for my day-to-day PC usage to accesses different Windows settings and apps efficiently.
If you are looking to be productive, then I will recommend you to memorize Run commands. To get you started, I will list some of the frequently used commands that I find most useful for day-to-day use.
How to open the Run dialog?
To use Run commands, you need to know how to open the Run dialog to enter the commands. There are two ways to access the Run dialog in Windows 10.
You can either press the Windows+R keys on the keyboard or right-click on the start menu and select Run from the menu.
I will recommend you to use the keyboard shortcut as it’s much faster and you won’t have to use the mouse. Once the Run dialog is open, enter any of the below mentioned commands and press the Enter key or click on the OK button to execute it.
#1. Access System Configuration — “msconfig”
Starting with my favorite command, the System Configuration window consists of multiple tabs to manage boot settings and background services.
If you have a dual boot setup or often need to access safe mode, you will often need to access these settings. Don’t forget to check its Tools section for convenient access to some of the most powerful Windows tools.
#2. Access Resource Monitor — “resmon”
A very powerful app to see real-time information about your system resources like CPU, RAM, disk, and network. For any computer hanging or performance-related issues, this is the best tool to get the information you need.
#3. Open System Information — “msinfo32”
System Information app offers extensive information about both the hardware and software of your PC. It’s a must-know command if you need to see the specs of any PC. The information is well laid out using dedicated categories, and you can export the information to a file to share with anyone — perfect for getting online tech assistance.
#4. Access Backup and Restore window — “sdclt”
It opens the backup and restores window where you can either set up a backup of your PC or restore it from an old backup if there is a problem with your PC.
#5. Access mouse properties — “main.cpl”
You can control all the settings related to your computer mouse here. This includes mouse speed, buttons, wheel, and pointer, etc.
#6. Open Windows Registry — “regedit”
If you ever need to access the Windows registry to tweak something, this is the easiest way to do it. I didn’t even know other ways to access the Registry until recently, and I often mess around in the Registry. Other ways are simply too cumbersome to use.
#7. Access System Properties — “sysdm.cpl”
Another powerful settings window to manage system protection and remote connection features. I personally access it often to manage the Performance settings under the Advanced tab. You can manage some interesting performance-boosting options there.
#8. Manage Windows Power options — “powercfg.cpl”
You will find all the options to manage your PC’s power options here. There are a plethora of options to both save power or get better performance. Check this guide to optimize the power options as you find best.
#9. Open Windows Features — “optionalfeatures”
Here you can disable/enable some of the most advanced features of Windows. I wouldn’t recommend you to mess around here if you don’t know what you are doing. You will need to use this window if you ever need to enable features like Telnet client or Hyper-V.
#10. Open Magnifier — “magnify”
This opens the Windows magnifier to magnify the content on the screen up to 1600% if needed. It also has a screen reader built-in to read aloud text on the screen.
#11. Open Character Map app — “charmap”
Windows Character Maps lets you access All the characters in the font of your choice to easily use anywhere you like. You can either copy the character or learn its Alt code to enter anywhere you like. Using the search bar is the easiest way to find the character you need.
#12. Access Network Connections — “ncpa.cpl”
Here you can manage your current network connection and fix any problem with the network device. You can enable/disable the network, check the current status, bridge connections, or see your Wi-Fi password.
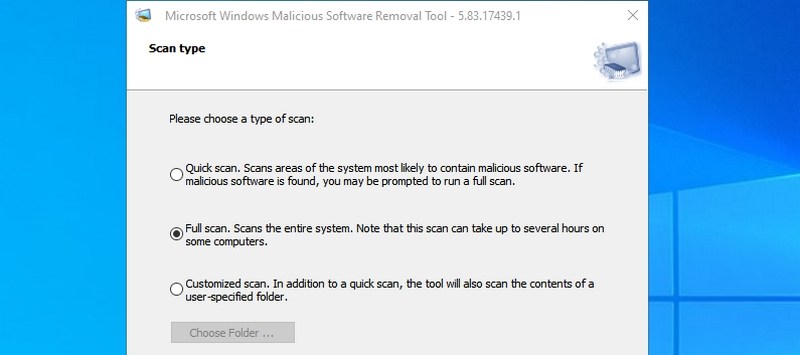
#13. Run Malicious Software Removal Tool — “mrt”
It’s an on-demand virus removal tool provided by Microsoft to scan your PC and find any malicious software. If you think your PC got infected by a virus, you can quickly launch this tool to scan your PC.
You can also consider installing antivirus software to keep your Windows computer safe.
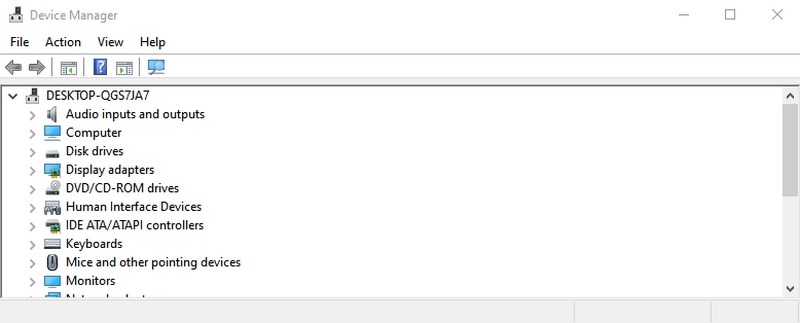
#14. Open Device Manager — “devmgmt.msc”
Device Manager is the go-to place to manage everything related to your hardware components and their drivers. You can enable/disable hardware components or manage their drivers, like uninstalling or updating them.
#15. Manage User Accounts — “netplwiz”
You can quickly manage user accounts here, such as adding a new account or user account types like Administrator or Standard. You can also change the user accounts password here and manage their security.
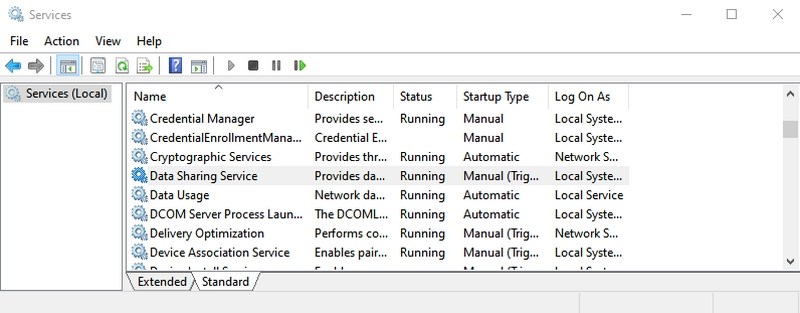
#16. Open Services app — “services.msc”
This app lists all the services that work in the background without an interface and make all the features work in Windows. Again, you shouldn’t mess with any services if you don’t know what you are doing. However, you can click on a service to learn what it does in the left panel. There are many services that you can enable/disable depending on your need. For example, I have disabled the Bluetooth service as I don’t use it.
#17. Access Programs and Features window — “appwiz.cpl”
Although Windows 10 has its own setting to uninstall an app, I still use this command as it only shows third-party apps. The default Windows uninstaller shows all apps, including built-in apps, which are 30+. It can be difficult to always go through so many apps to uninstall a recently installed app. This command makes the process a snap.
#18. Open Control Panel — “control”
This command didn’t hold much value in the older version of Windows as you could easily access Control Panel using different ways. However, in Windows 10, Microsoft promotes the new Settings over the old Control Panel, so it doesn’t offer an easy way to access the Control Panel. This simple command lets you easily access it.
#19. Open current user folder — “.” (period)
We have to access the user folder quite often in Windows, but going through the explorer to access it isn’t needed. Just type a period in the Run dialog, and the current user’s folder will open up.
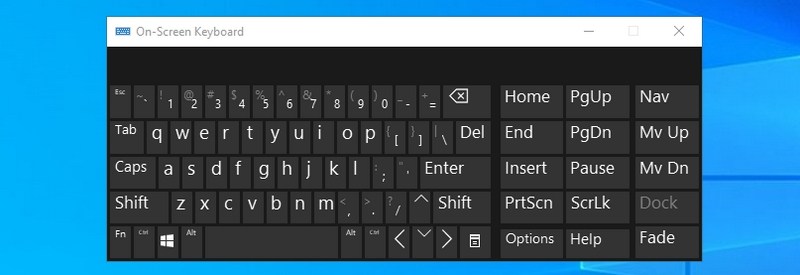
#20. Open On-Screen Keyboard — “osk”
If you want to use the on-screen keyboard, then using the Run command is one of the quickest ways to do it.
#21. Open Snipping Tool — “snippingtool”
Snipping Tool is still the go-to tool for taking screenshots in Windows 10 without using a third-party app. If you use the Snipping Tool for taking screenshots, then this Run command will make it easier.
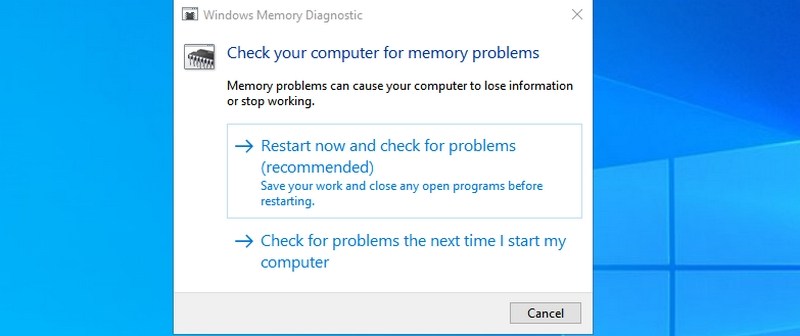
#22. Open Windows Memory Diagnostic — “mdsched”
If you think there is a problem with your RAM, this tool can check your RAM and possibly fix the problem or let you know there is an issue. If you start seeing sudden freezes or crashes, it could mean there is a problem with your RAM.
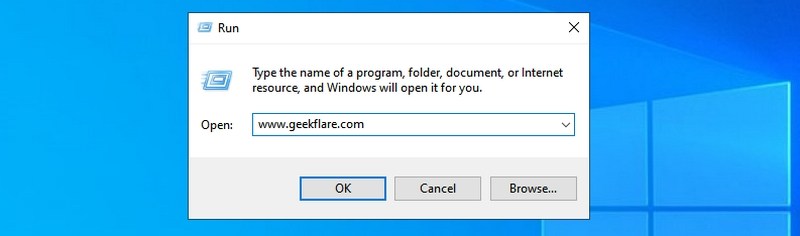
#23. Open any website — “Insert website URL”
You can also enter the URL of any website in the Run dialog, and it will open it in your default browser. For example, if you type www.geekflare.com in the Run command, it will open the Geekflare home page in your default browser.
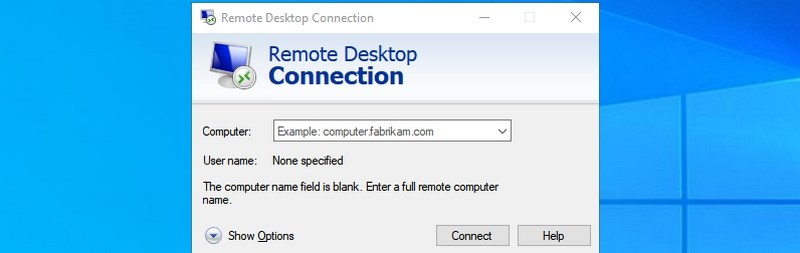
#24. Open Remote Desktop Connection — “mstsc”
You can use this feature to remotely connect to another PC and take full control over it. You’ll have to set up both PCs for the remote connection first, though. This Run command just makes the process easier.
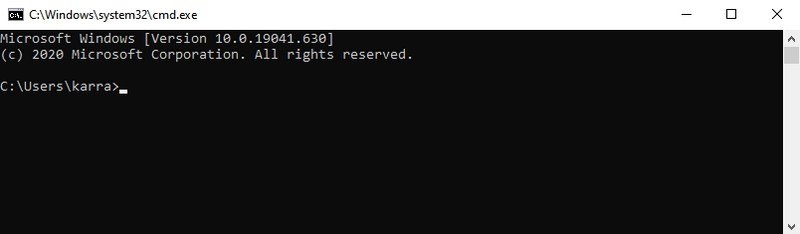
#25. Open Command Prompt — “cmd”
Unlike PowerShell, you can’t access the Command Prompt by right-clicking on the start menu anymore. If you prefer using the Command Prompt over PowerShell to execute commands, this is one of the easier ways to open the Command Prompt.
Wrapping up
The cool thing about Run is that it remembers all the commands you type in it. Therefore, you will only have to type the first letter to enter the command in the future.
I also believe Run commands are more important in Windows 10 as it heavily promotes the use of its default Settings app. Most of the settings and apps that I have mentioned above are more difficult to access Windows 10.
Next, explore some of the best NirSoft utilities for Windows.