- Windows system message log
- Как открыть в просмотр событий
- Фильтрация в просмотре событий
- Посмотреть логи windows PowerShell
- Дополнительные продукты
- Удаленный просмотр логов
- Configuring Message Logging
- Enabling Message Logging
- Logging Levels and Options
- Service Level
- Transport Level
- Malformed Level
- Other Options
Windows system message log
Всем привет, тема стать как посмотреть логи windows. Что такое логи думаю знают все, но если вдруг вы новичок, то логи это системные события происходящие в операционной системе как Windows так и Linux, которые помогают отследить, что, где и когда происходило и кто это сделал. Любой системный администратор обязан уметь читать логи windows.
Примером из жизни может служить ситуация когда на одном из серверов IBM, выходил из строя диск и для технической поддержки я собирал логи сервера, для того чтобы они могли диагностировать проблему. За собирание и фиксирование логов в Windows отвечает служба Просмотр событий. Просмотр событий это удобная оснастка для получения логов системы.
Как открыть в просмотр событий
Зайти в оснастку Просмотр событий можно очень просто, подойдет для любой версии Windows. Нажимаете волшебные кнопки
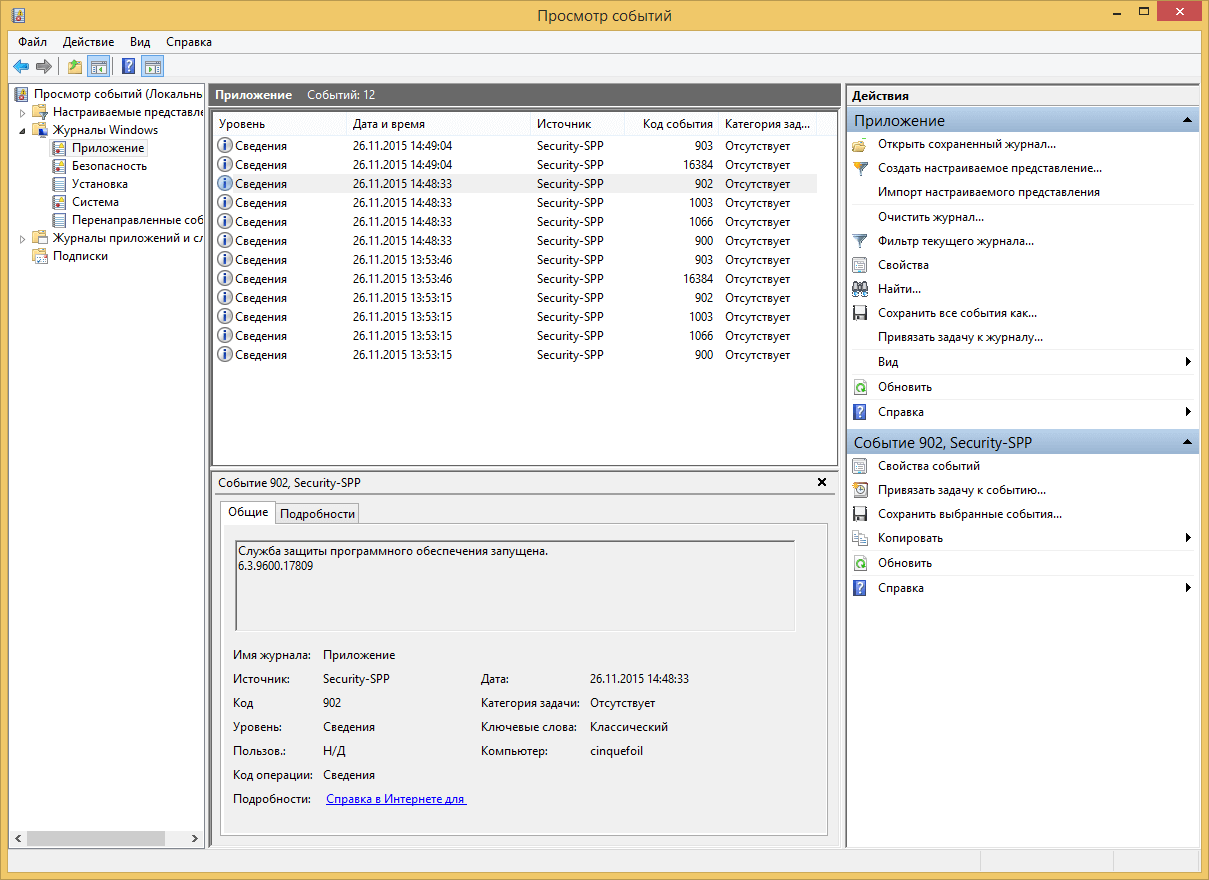
Откроется у вас окно просмотр событий windows в котором вам нужно развернуть пункт Журналы Windows. Пробежимся по каждому из журналов.
Журнал Приложение, содержит записи связанные с программами на вашем компьютере. В журнал пишется когда программа была запущена, если запускалась с ошибкоу, то тут это тоже будет отражено.
Журнал аудит, нужен для понимания кто и когда что сделал. Например вошел в систему или вышел, попытался получить доступ. Все аудиты успеха или отказа пишутся сюда.
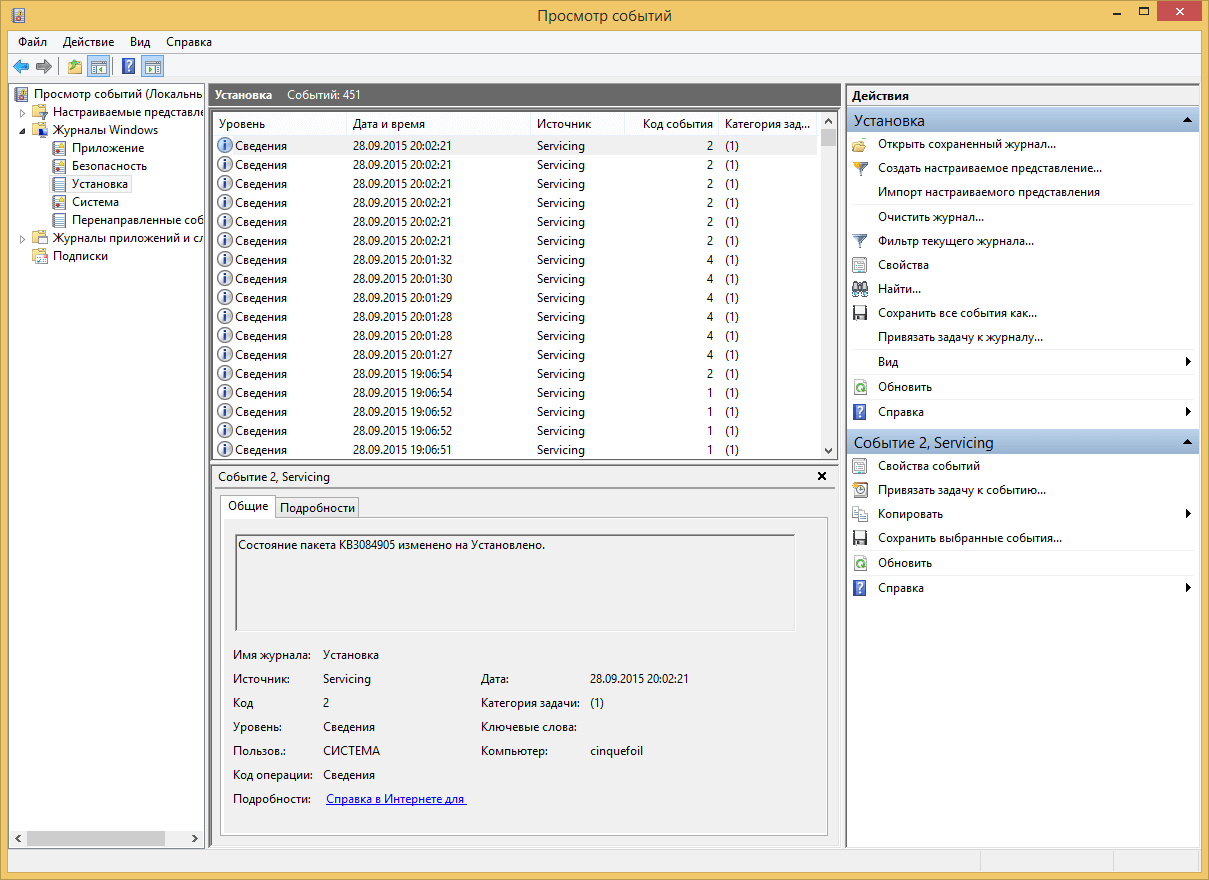
Пункт Установка, в него записывает Windows логи о том что и когда устанавливалось Например программы или обновления.
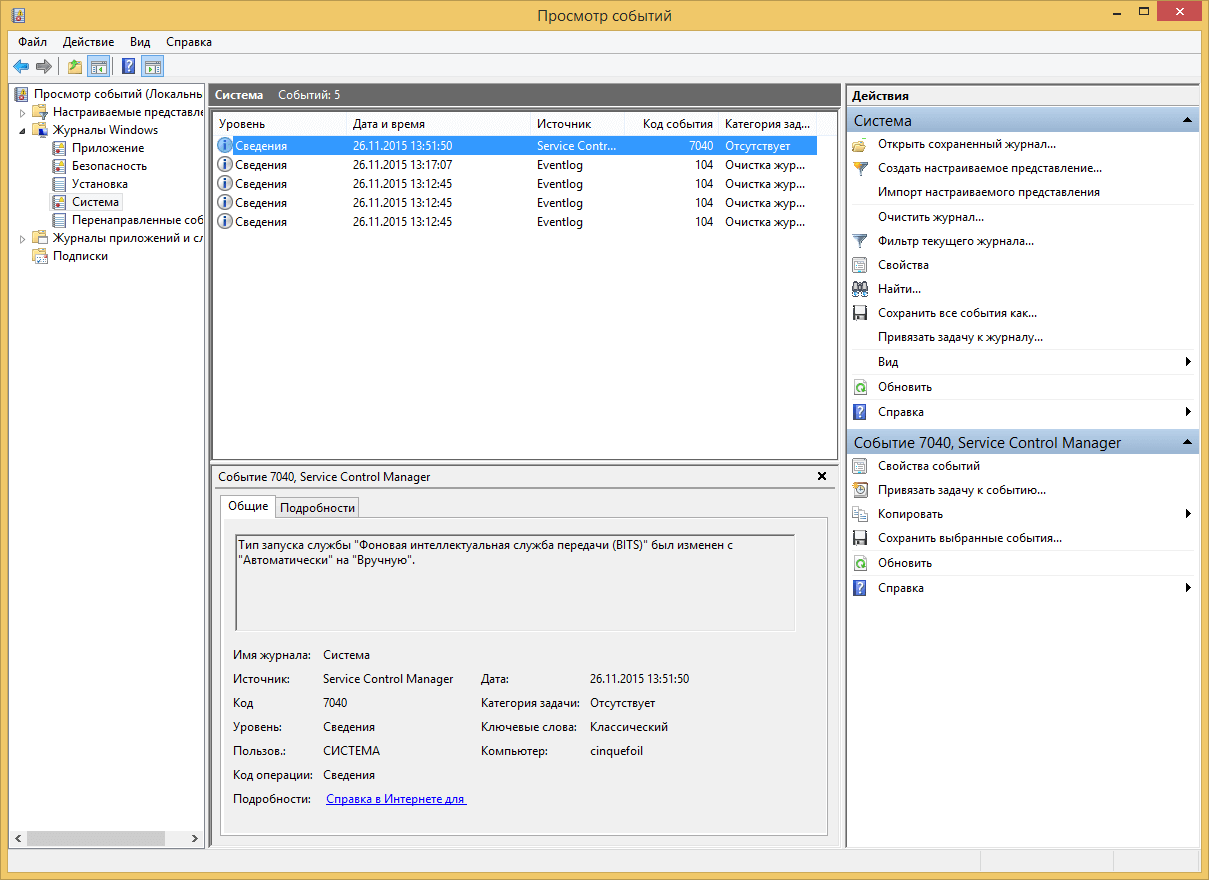
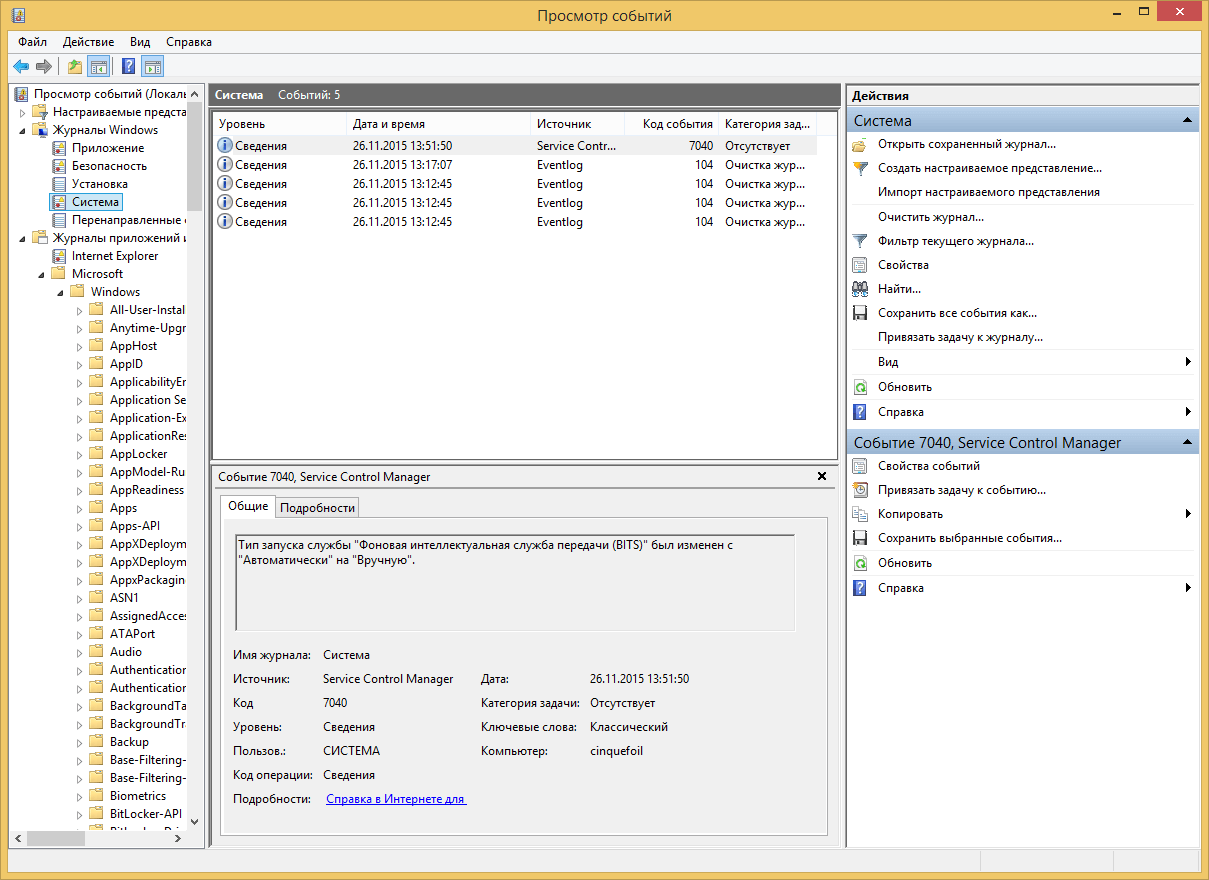
Самый важный журнал Это система. Сюда записывается все самое нужное и важное. Например у вас был синий экран bsod, и данные сообщения что тут заносятся помогут вам определить его причину.
Так же есть логи windows для более специфических служб, например DHCP или DNS. Просмотр событий сечет все :).
Фильтрация в просмотре событий
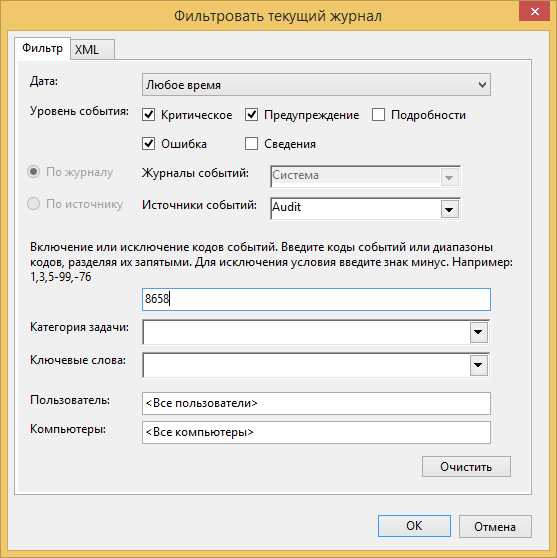
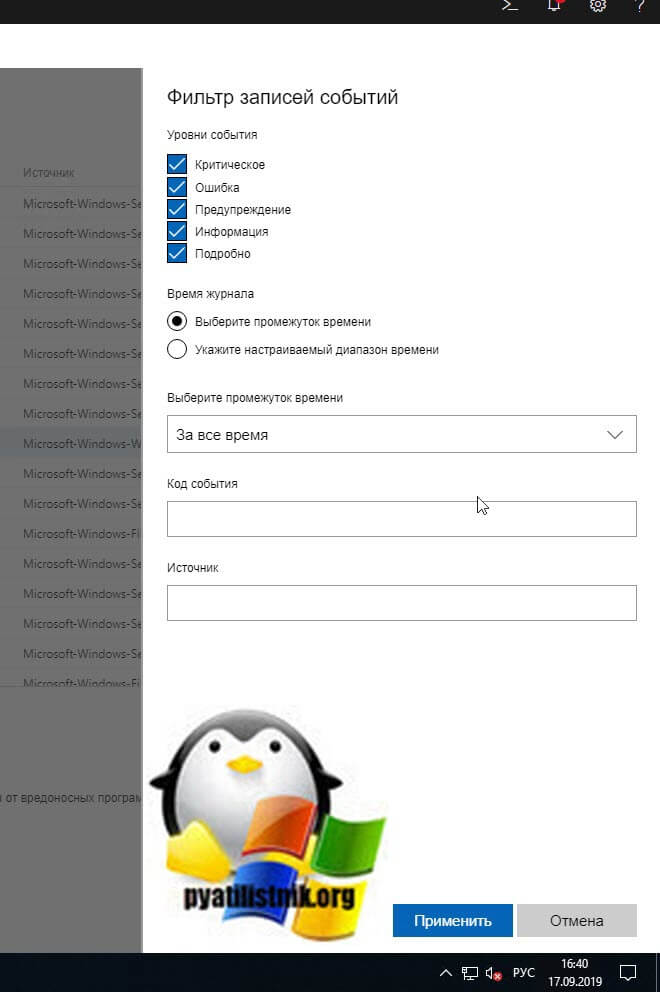
Предположим у вас в журнале Безопасность более миллиона событий, наверняка вы сразу зададите вопрос есть ли фильтрация, так как просматривать все из них это мазохизм. В просмотре событий это предусмотрели, логи windows можно удобно отсеять оставив только нужное. Справа в области Действия есть кнопка Фильтр текущего журнала.
Вас попросят указать уровень событий:
- Критическое
- Ошибка
- Предупреждение
- Сведения
- Подробности
Все зависит от задачи поиска, если вы ищите ошибки, то смысла в других типах сообщение нету. Далее можете для того чтобы сузить границы поиска просмотра событий укзать нужный источник событий и код.
Так что как видите разобрать логи windows очень просто, ищем, находим, решаем. Так же может быть полезным быстрая очистка логов windows:
Посмотреть логи windows PowerShell
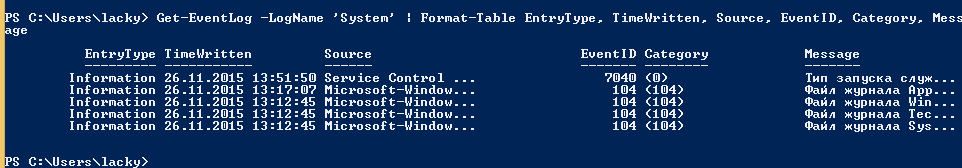
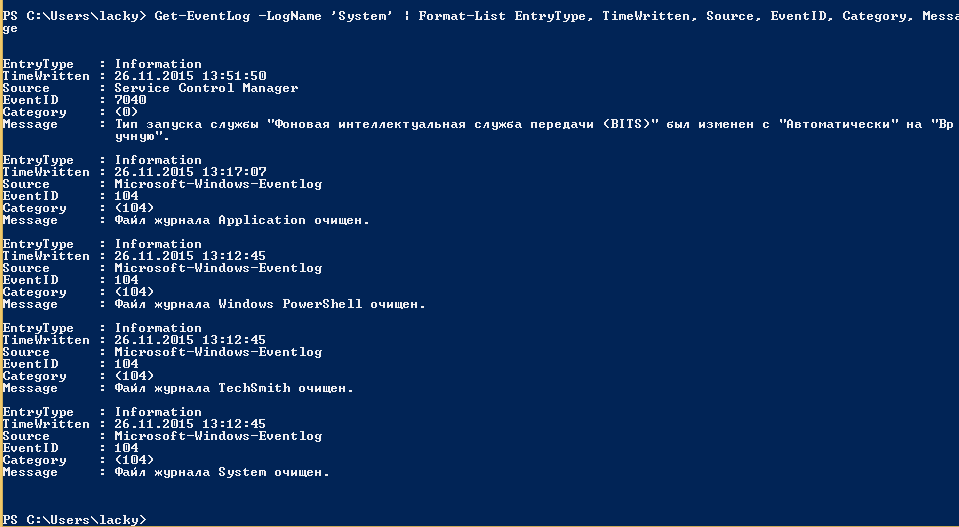
Было бы странно если бы PowerShell не умел этого делать, для отображения log файлов открываем PowerShell и вводим вот такую команду
В итоге вы получите список логов журнала Система
Тоже самое можно делать и для других журналов например Приложения
небольшой список абревиатур
- Код события — EventID
- Компьютер — MachineName
- Порядковый номер события — Data, Index
- Категория задач — Category
- Код категории — CategoryNumber
- Уровень — EntryType
- Сообщение события — Message
- Источник — Source
- Дата генерации события — ReplacementString, InstanceID, TimeGenerated
- Дата записи события — TimeWritten
- Пользователь — UserName
- Сайт — Site
- Подразделение — Conteiner
Например, для того чтобы в командной оболочке вывести события только со столбцами «Уровень», «Дата записи события», «Источник», «Код события», «Категория» и «Сообщение события» для журнала «Система», выполним команду:
Если нужно вывести более подробно, то заменим Format-Table на Format-List
Как видите формат уже более читабельный.
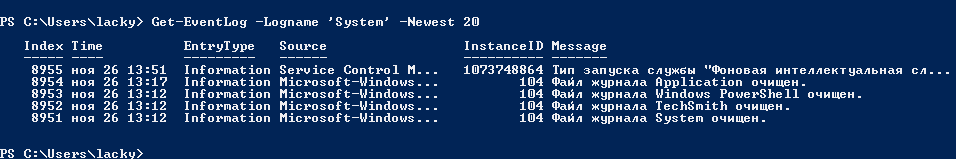
Так же можно пофильтровать журналы например показать последние 20 сообщений
Или выдать список сообщение позднее 1 ноября 2014
Дополнительные продукты
Так же вы можете автоматизировать сбор событий, через такие инструменты как:
- Комплекс мониторинга Zabbix
- Через пересылку событий средствами Windows на сервер коллектор
- Через комплекс аудита Netwrix
- Если у вас есть SCOM, то он может агрегировать любые логи Windows платформ
- Любые DLP системы
Так что вам выбирать будь то просмотр событий или PowerShell для просмотра событий windows, это уже ваше дело. Материал сайта pyatilistnik.org
Удаленный просмотр логов
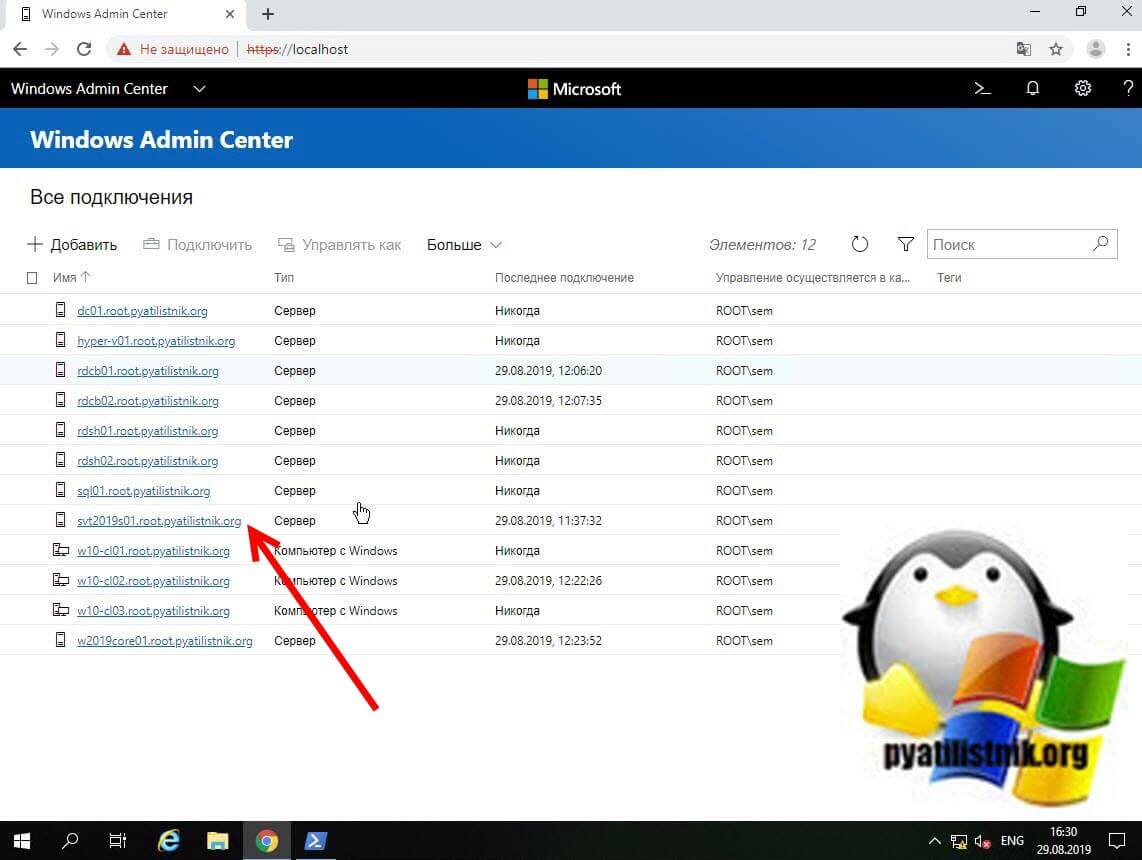
Не так давно в появившейся операционной системе Windows Server 2019, появился компонент удаленного администрирования Windows Admin Center. Он позволяет проводить дистанционное управление компьютером или сервером, подробнее он нем я уже рассказывал. Тут я хочу показать, что поставив его себе на рабочую станцию вы можете подключаться из браузера к другим компьютерам и легко просматривать их журналы событий, тем самым изучая логи Windows. В моем примере будет сервер SVT2019S01, находим его в списке доступных и подключаемся (Напомню мы так производили удаленную настройку сети в Windows).
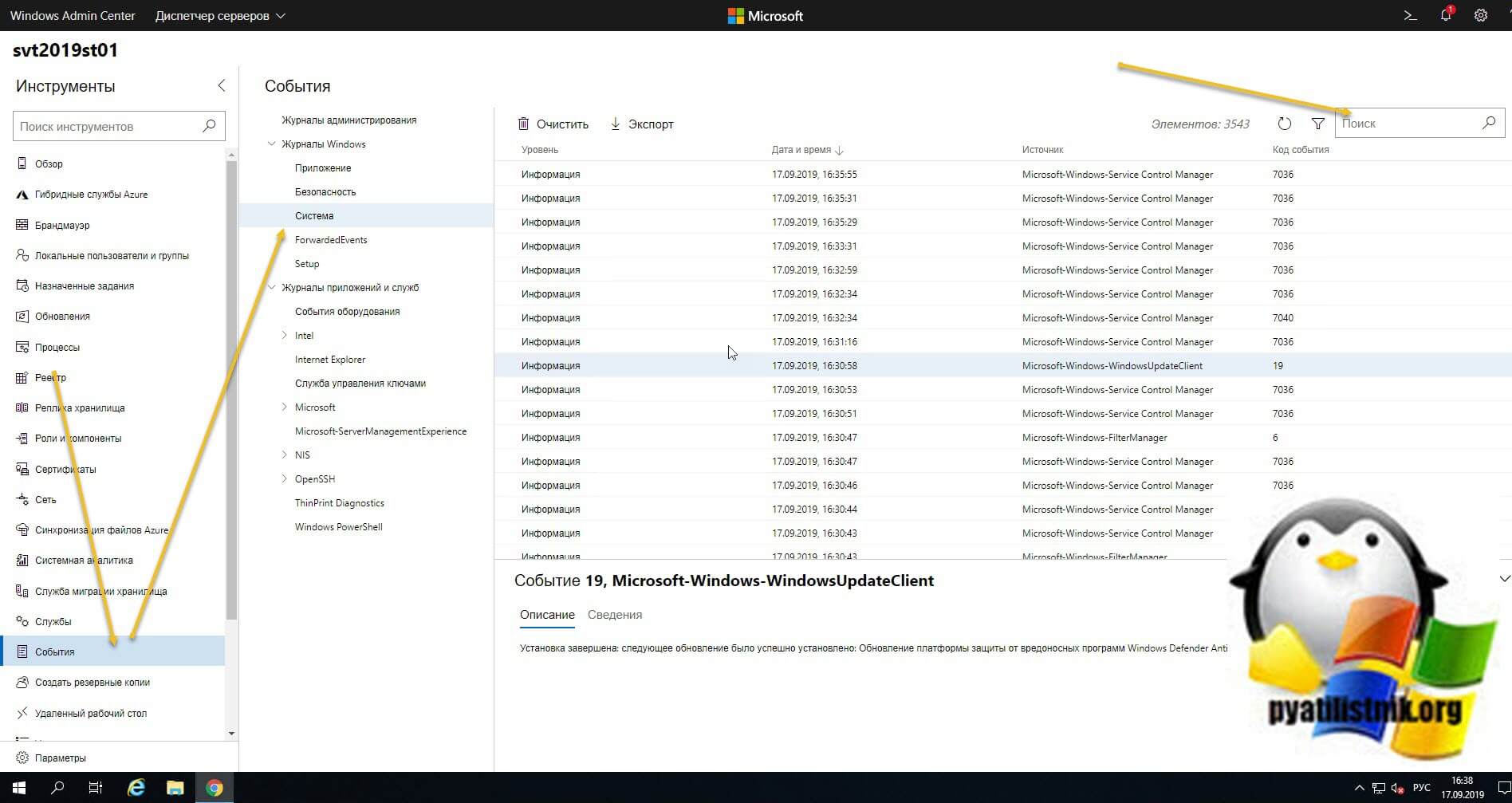
Далее вы выбираете вкладку «События», выбираете нужный журнал, в моем примере я хочу посмотреть все логи по системе. С моей точки зрения тут все просматривать куда удобнее, чем из просмотра событий. Плюсом будет, то что вы это можете сделать из любого телефона или планшета. В правом углу есть удобная форма поиска
Если нужно произвести более тонкую фильтрацию логов, то вы можете воспользоваться кнопкой фильтра.
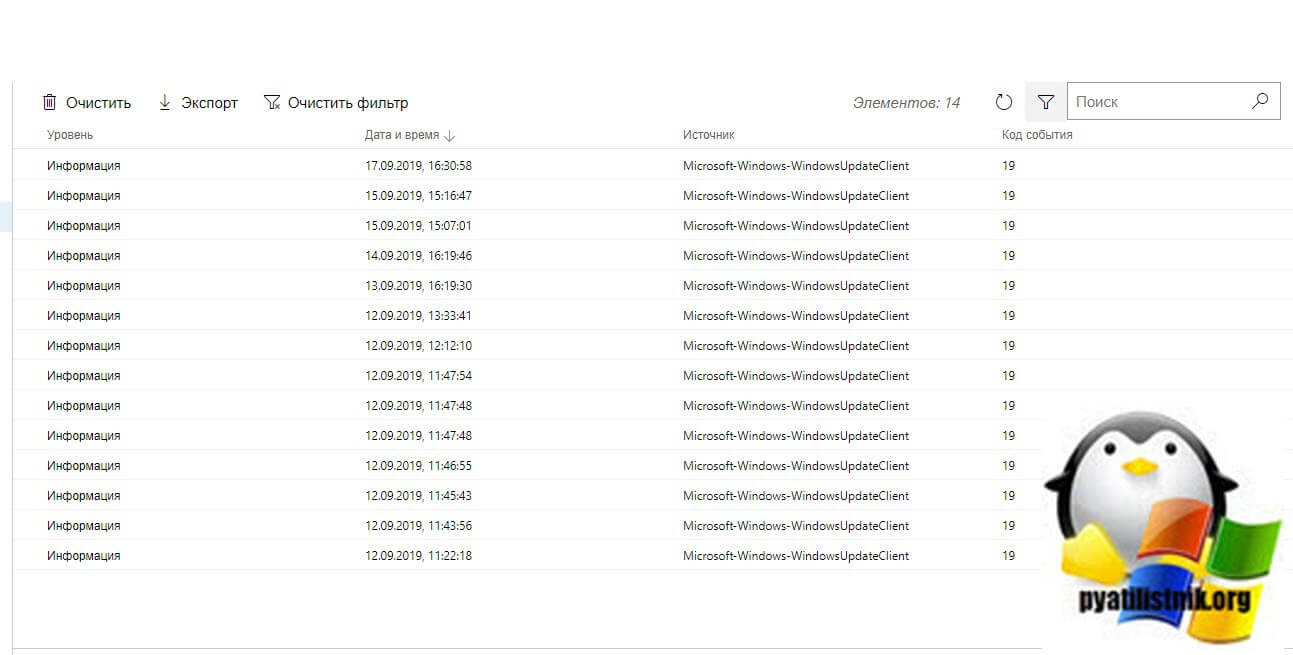
Тут вы так же можете выбрать уровень события, например оставив только критические и ошибки, задать временной диапазон, код событий и источник.
Вот пример фильтрации по событию 19.
Очень удобно экспортировать полностью журнал в формат evxt, который потом легко открыть через журнал событий. Так, что Windows Admin Center, это мощное средство по просмотру логов.
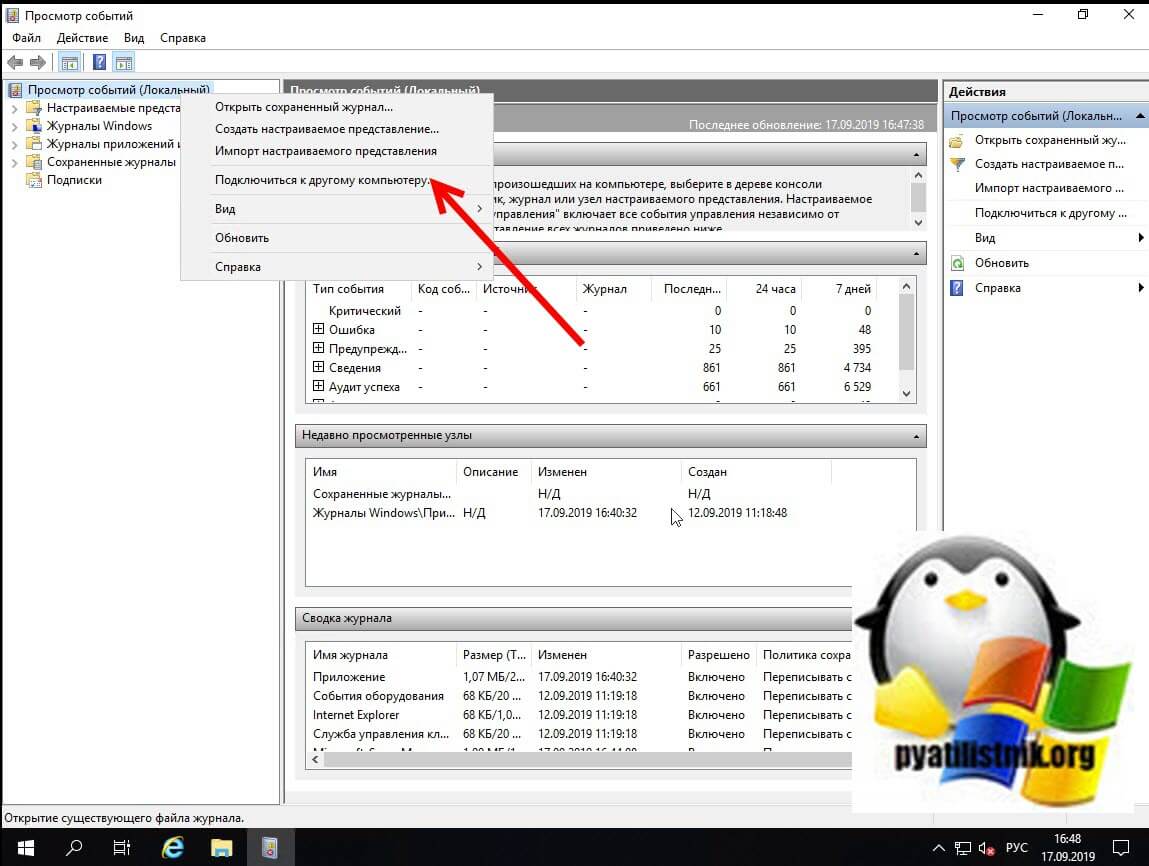
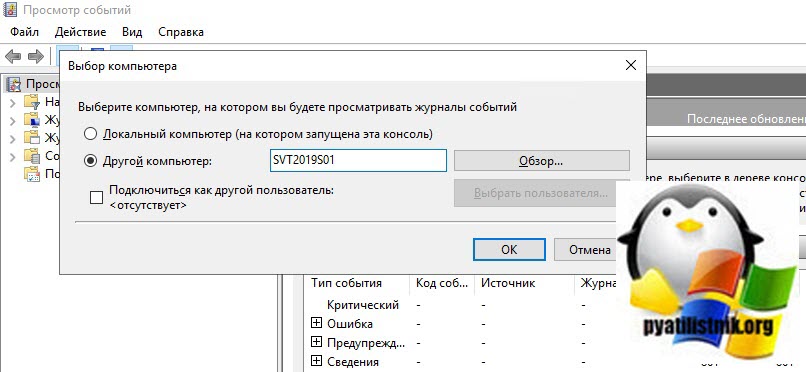
Второй способ удаленного просмотров логов Windows, это использование оснастки управление компьютером или все той же «Просмотр событий». Чтобы посмотреть логи Windows на другом компьютере или сервере, в оснастке щелкните по верхнему пункту правым кликом и выберите из контекстного меню «Подключиться к другому компьютеру«.
Указываем имя другого компьютера, в моем примере это будет SVT2019S01
Если все хорошо и нет блокировок со стороны брандмауэра или антивируса, то вы попадете в удаленный просмотр событий .если будут блокировки, то получите сообщение по типу, что не пролетает трафик COM+.
Configuring Message Logging
This topic describes how you can configure message logging for different scenarios.
Enabling Message Logging
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) does not log messages by default. To activate message logging, you must add a trace listener to the System.ServiceModel.MessageLogging trace source and set attributes for the element in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to enable logging and specify additional options.
For more information about message logging settings, see Recommended Settings for Tracing and Message Logging.
You can use add to specify the name and type of the listener you want to use. In the example configuration, the Listener is named «messages» and adds the standard .NET Framework trace listener ( System.Diagnostics.XmlWriterTraceListener ) as the type to use. If you use System.Diagnostics.XmlWriterTraceListener , you must specify the output file location and name in the configuration file. This is done by setting initializeData to the name of the log file. Otherwise, the system throws an exception. You can also implement a custom listener that emits logs to a default file.
Because message logging accesses disk space, you should limit the number of messages that are written to disk for a particular service. When the message limit is reached, a trace at the Information level is produced and all message logging activities stop.
The logging level, as well as the additional options, are discussed in the Logging Level and Options section.
The switchValue attribute of a source is only valid for tracing. If you specify a switchValue attribute for the System.ServiceModel.MessageLogging trace source as follows, it has no effect.
If you want to disable the trace source, you should use the logMessagesAtServiceLevel , logMalformedMessages , and logMessagesAtTransportLevel attributes of the messageLogging element instead. You should set all these attributes to false . This can be done by using the configuration file in the previous code example, through the Configuration Editor UI interface, or using WMI. For more information about the Configuration Editor tool, see Configuration Editor Tool (SvcConfigEditor.exe). For more information about WMI, see Using Windows Management Instrumentation for Diagnostics.
Logging Levels and Options
For incoming messages, logging happens immediately after the message is formed, immediately before the message gets to user code in the service level, and when malformed messages are detected.
For outgoing messages, logging happens immediately after the message leaves user code and immediately before the message goes on the wire.
WCF logs messages at two different levels, service and transport. Malformed messages are also logged. The three categories are independent from each other and can be activated separately in configuration.
You can control the logging level by setting the logMessagesAtServiceLevel , logMalformedMessages , and logMessagesAtTransportLevel attributes of the messageLogging element.
Service Level
Messages logged at this layer are about to enter (on receiving) or leave (on sending) user code. If filters have been defined, only messages that match the filters are logged. Otherwise, all messages at the service level are logged. Infrastructure messages (transactions, peer channel, and security) are also logged at this level, except for Reliable Messaging messages. On streamed messages, only the headers are logged. In addition, secure messages are logged decrypted at this level.
Transport Level
Messages logged at this layer are ready to be encoded or decoded for or after transportation on the wire. If filters have been defined, only messages that match the filters are logged. Otherwise, all messages at the transport layer are logged. All infrastructure messages are logged at this layer, including reliable messaging messages. On streamed messages, only the headers are logged. In addition, secure messages are logged as encrypted at this level, except if a secure transport such as HTTPS is used.
Malformed Level
Malformed messages are messages that are rejected by the WCF stack at any stage of processing. Malformed messages are logged as-is: encrypted if they are so, with non-proper XML, and so on. maxSizeOfMessageToLog defined the size of the message to be logged as CDATA. By default, maxSizeOfMessageToLog is equal to 256K. For more information about this attribute, see the Other Options section.
Other Options
In addition to the logging levels, the user can specify the following options:
Log Entire Message ( logEntireMessage attribute): This value specifies whether the entire message (message header and body) is logged. The default value is false , meaning that only the header is logged. This setting affects service and transport message logging levels..
Max messages to log ( maxMessagesToLog attribute): This value specifies the maximum number of messages to log. All messages (service, transport, and malformed messages) are counted towards this quota. When the quota is reached, a trace is emitted and no additional message is logged. The default value is 10000.
Max size of message to log ( maxSizeOfMessageToLog attribute): This value specifies the maximum size of messages to log in bytes. Messages that exceed the size limit are not logged, and no other activity is performed for that message. This setting affects all trace levels. If ServiceModel tracing is on, a Warning level trace is emitted at the first logging point (ServiceModelSend* or TransportReceive) to notify the user. The default value for service level and transport level messages is 256K, while the default value for malformed messages is 4K.
The message size that is computed to compare against maxSizeOfMessageToLog is the message size in memory before serialization. This size can differ from the actual length of the message string that is being logged, and in many occasions is bigger than the actual size. As a result, messages may not be logged. You can account for this fact by specifying the maxSizeOfMessageToLog attribute to be 10% larger than the expected message size. In addition, if malformed messages are logged, the actual disk space utilized by the message logs can be up to 5 times the size of the value specified by maxSizeOfMessageToLog .
If no trace listener is defined in the configuration file, no logging output is generated regardless of the specified logging level.
Message logging options, such as the attributes described in this section, can be changed at runtime using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). This can be done by accessing the AppDomainInfo instance, which exposes these Boolean properties: LogMessagesAtServiceLevel , LogMessagesAtTransportLevel , and LogMalformedMessages . Therefore, if you configure a trace listener for message logging, but set these options to false in configuration, you can later change them to true when the application is running. This effectively enables message logging at runtime. Similarly, if you enable message logging in your configuration file, you can disable it at runtime using WMI. For more information, see Using Windows Management Instrumentation for Diagnostics.
The source field in a message log specifies in which context the message is logged: when sending/receiving a request message, for a request-reply or 1-way request, at service model or transport layer, or in the case of a malformed message.
For malformed messages, source is equal to Malformed . Otherwise, source has the following values based on the context.