- Windows system resource manager это
- Устанавливаем компонент диспетчер системных ресурсов
- Создание условия соответствия процессов
- Создание политик выделения ресурсов
- Ограничение лимита по процессорам
- Использование Диспетчера системных ресурсов Windows (WSRM) для распределения ресурсов в Windows Server 2008
- Windows System Resource Manager Overview
- Role/Feature description
- Practical applications
- Methods of resource management
- Built-in resource management policies
- Custom resource management
- Removed or deprecated functionality
Windows system resource manager это
Всем привет сегодня хочу рассказывать, о том как установить и настроить диспетчер системных ресурсов Windows server 2008 R2. Напомню, что это компонент, который позволяет ограничить Службы удаленных рабочих столов и пулы приложений служб IIS по процессорам и оперативной памяти, так как на моей практике, были случаи, что iis выедала всю ОЗУ и виртуальная машина просто висла на прочь. Ниже мы рассмотрим как этого избежать.
И так принцип ясен, создаем лимит по ресурсам для определенной службы. Для начала нужно установить диспетчер системных ресурсов, он есть только в Windows server 2008 R2 Enterprise и Datacenter.
Устанавливаем компонент диспетчер системных ресурсов
Открываем диспетчер сервера > Компоненты > Добавить компоненты
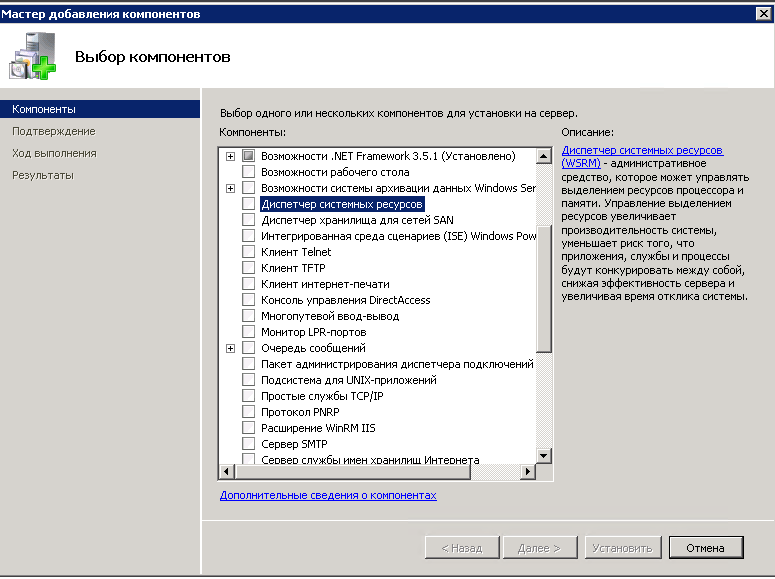
Выбираем диспетчер системных ресурсов и жмем далее.
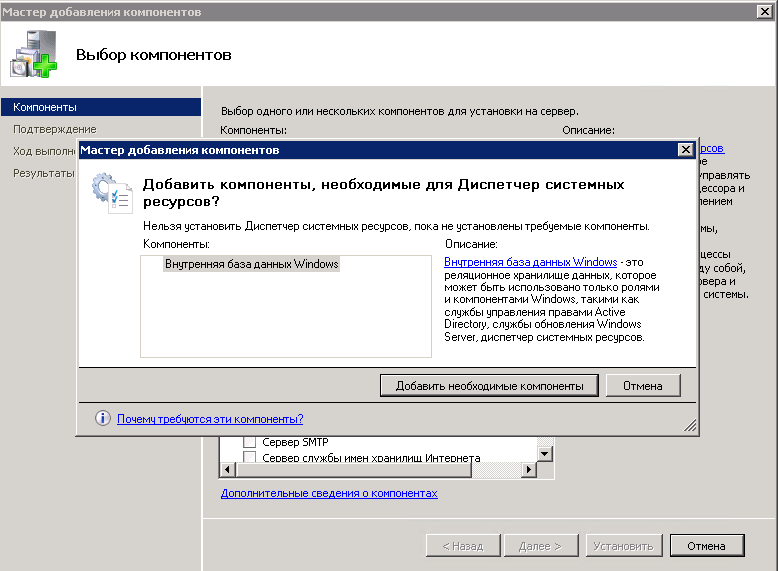
Вам покажут, что нужно добавить дополнительные компоненты.
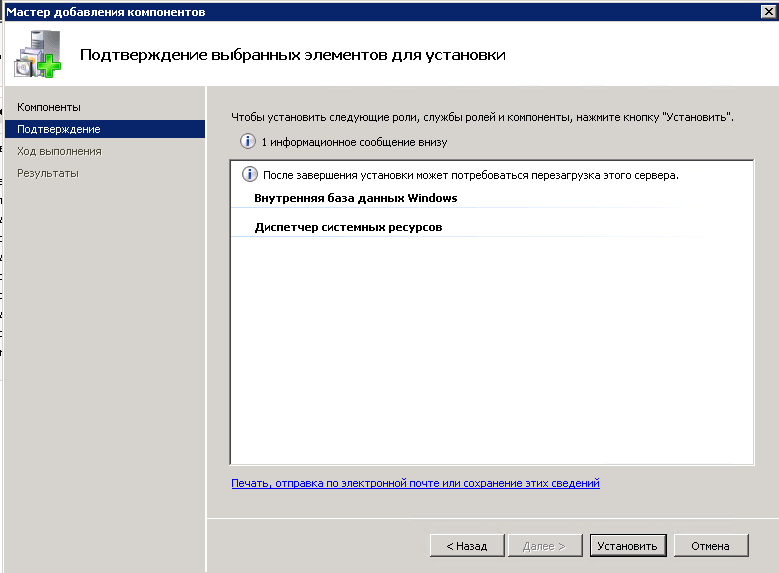
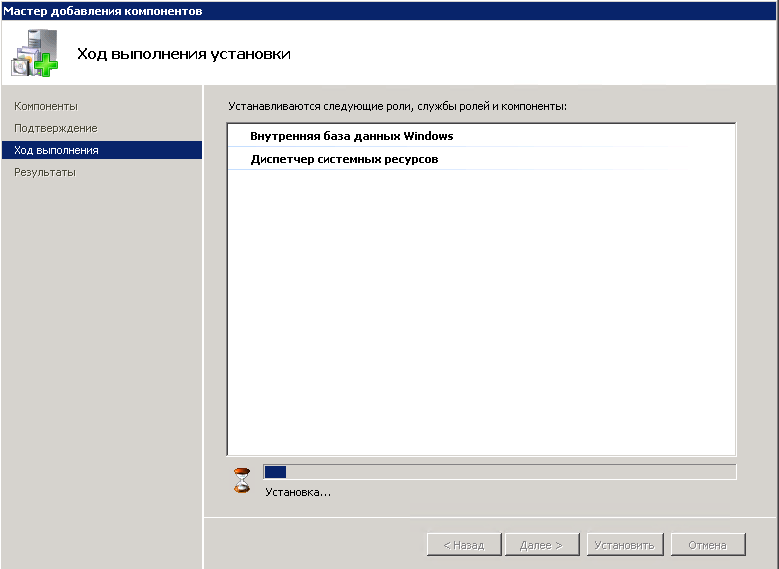
начнется процесс установки диспетчера системных ресурсов
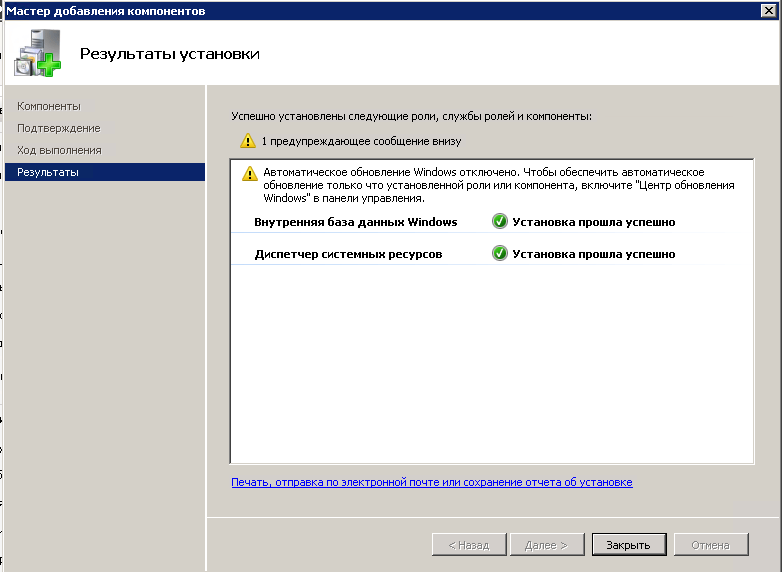
Через пару минут компонент будет добавлен, не забудьте проверить обновления Windows, может для него, что то найдется.
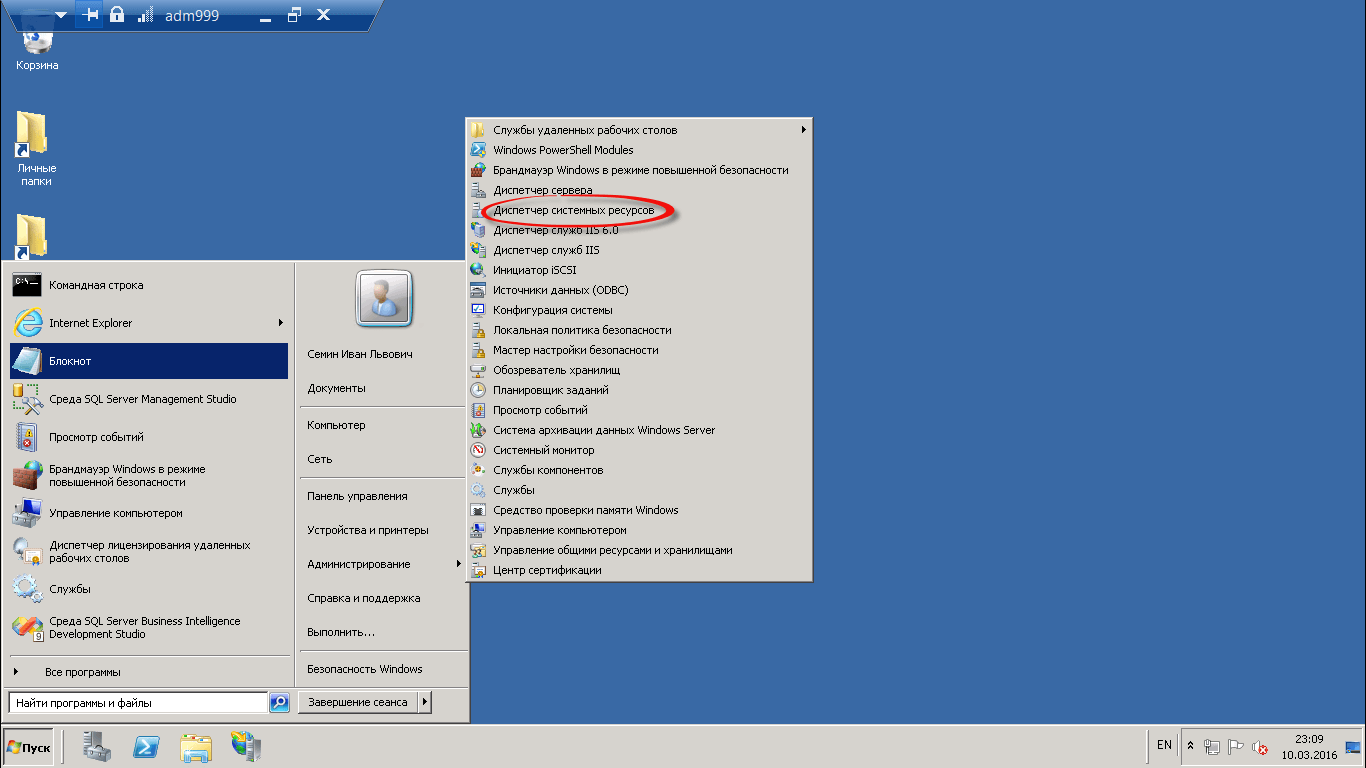
теперь давайте его запустим, для этого идем в пуск > Администрирование > диспетчер системных ресурсов
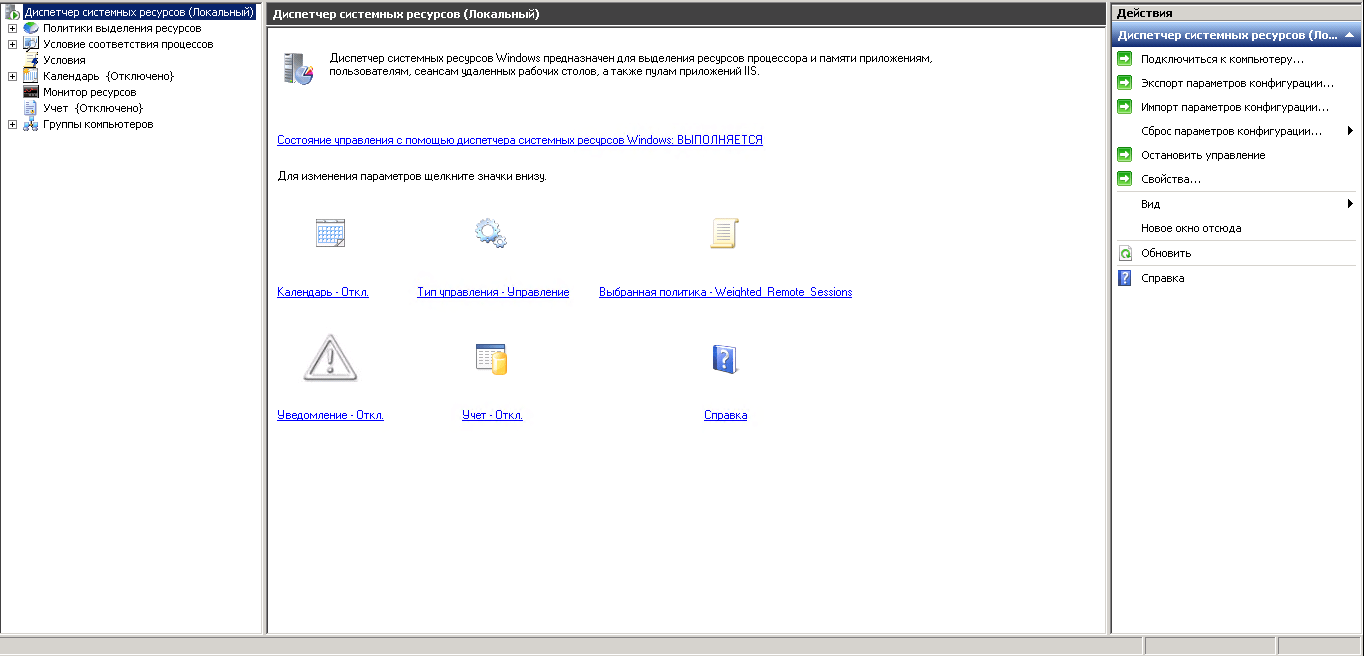
Вот как выглядит сама оснастка.
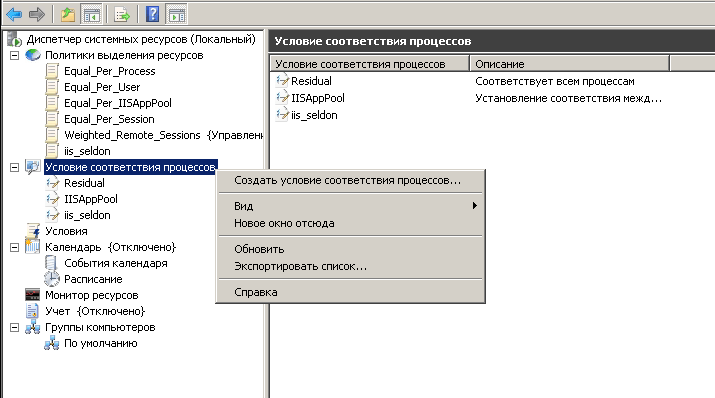
Создание условия соответствия процессов
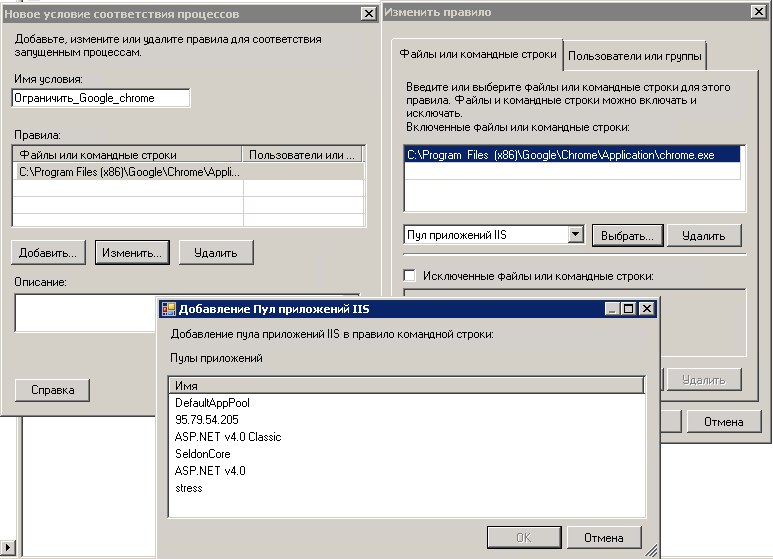
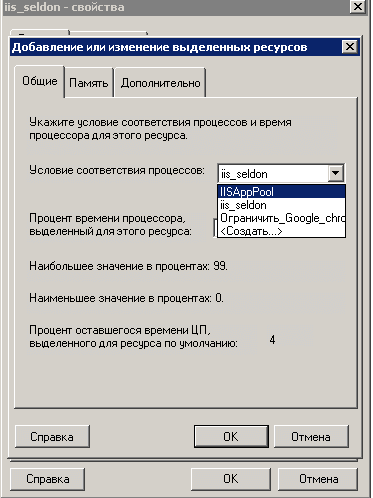
Первым делом в Windows System Resource Manager делается условие, что именно за процесс или сборник процессов вы хотите ограничить. Щелкаем правым кликом по условие соответствия процессов и выбираем создать.
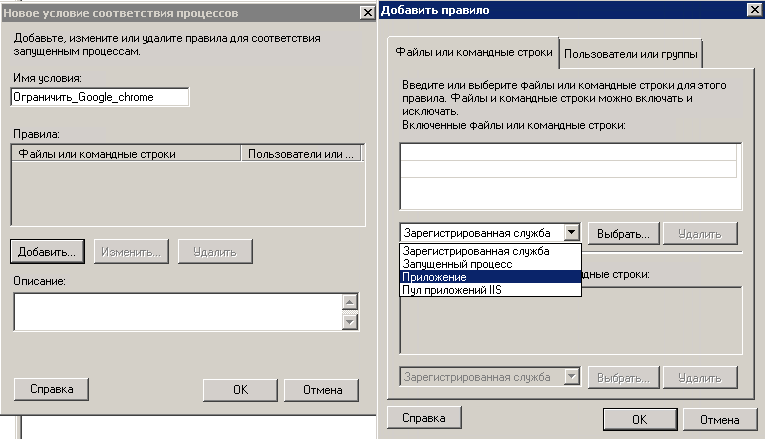
В открывшемся окне мастера введите понятное вам название, так как условий ограничения может быть много, чтобы у вас не было путаницы. Теперь жмете Добавить, и у вас на выбор 4 пункта
- Зарегистрированная служба
- Запущенный процесс
- Приложение
- Пул приложений IIS
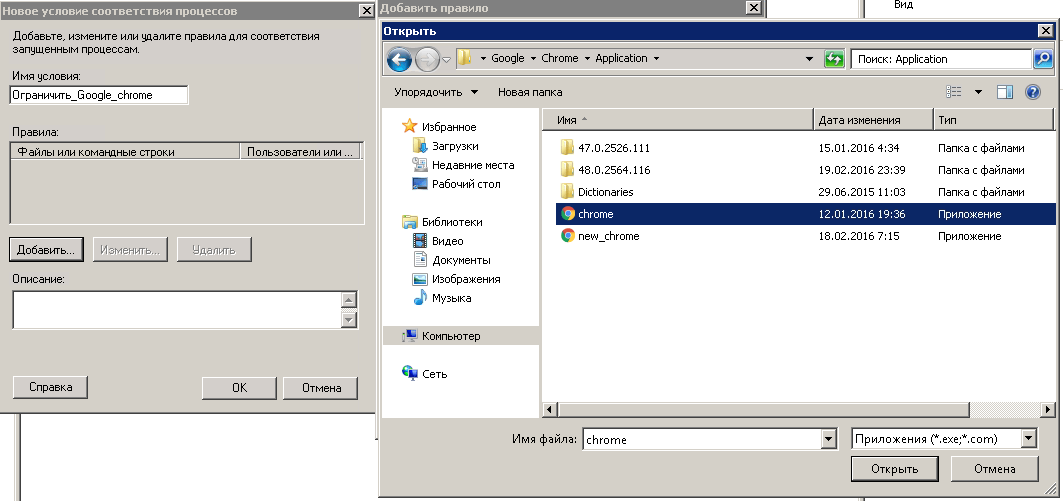
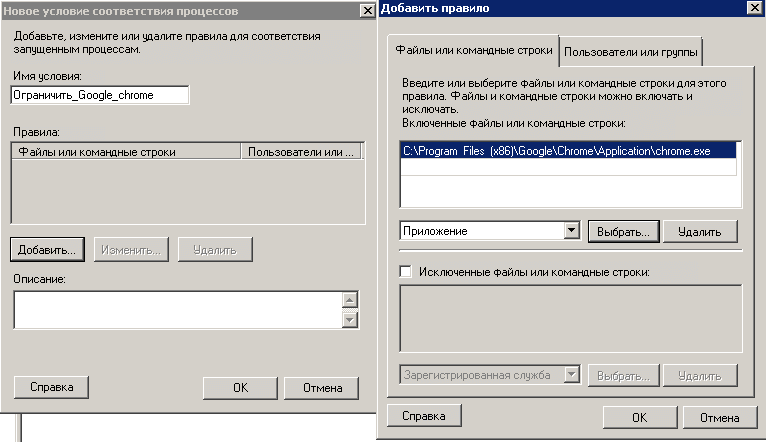
Я для примера буду ограничивать приложение Google Chrome. для этого его нужно выбрать.
При желании можно добавлять много приложений.
если вы будите ограничивать IIS, то Windows System Resource Manager позволяет ограничивать даже конкретные пулы.
Далее переходим к созданию политик.
Создание политик выделения ресурсов
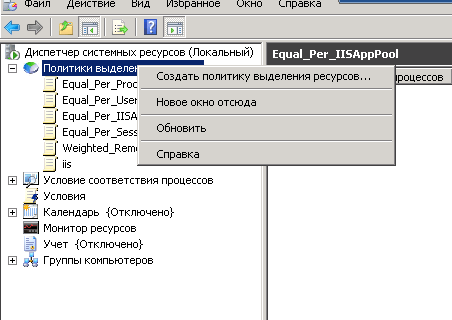
Для того, чтобы создать новую политику, щелкаем по корню правым кликом и выбираем Создать политику выделения ресурсов.
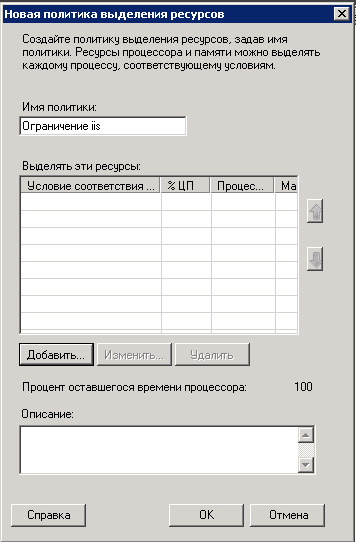
В мастере задаем имя политики и жмем добавить. Кстати если политик будет несколько, то их приоритет можно задавать с помощью стрелок.
У вас откроются 3 вкладки
- Общие > даст задать условие и ограничить процессоры
- Память > задать ограничение по памяти
- Дополнительно
Ограничение лимита по процессорам
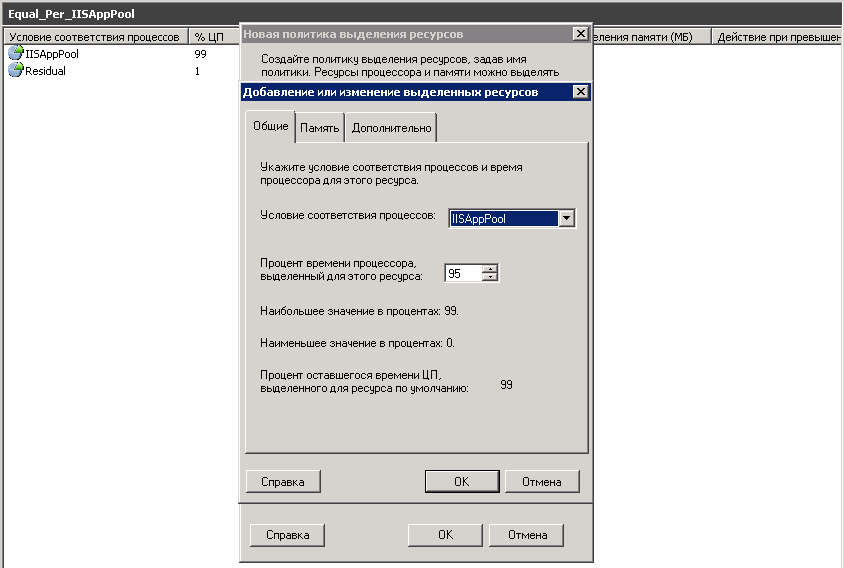
Я выбираю для примера IISAppPool и говорю, что он не может использовать более 95 процентов процессора. По сути вы указали максимальную величину процессорного времени, которое может потреблять выбранное приложение. При наличии всего одной политики вы можете установить для процессорного времени в любое значение от 0% до 99%.
Посмотрите еще параметр Процент оставшегося времени ЦП, это сколько процессорных мощностей у вас осталось. Простой пример вы задали политикой для приложения 25% из ресурсов вашего процессора, это значит что остальным приложениям будет доступно 74 процента один процент система оставляет себе на случай того, чтобы можно было достучаться до Windows System Resource Manager.
Но тут же можно и выбрать, то что создано заранее.
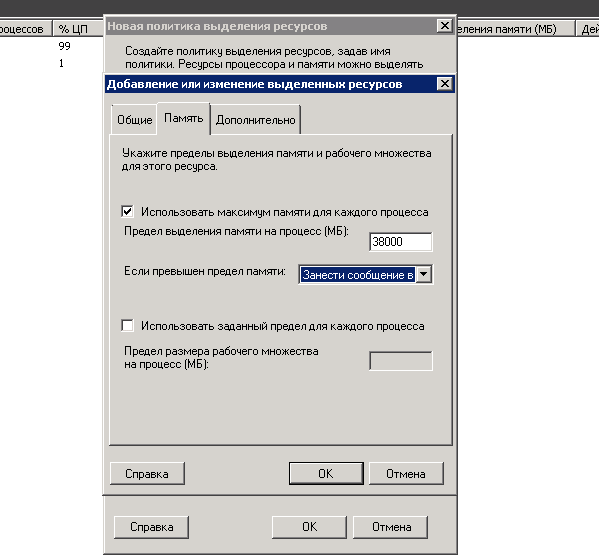
Теперь переходим на вкладку Память. Тут ставим галку Использовать максимум памяти для каждого процесса и выставляем лимит, а так же действие, что будет если будет превышен лимит, я выставил остановить..
С одной стороны, если приложение запущено на вашем сервере, то на это были причины. Поэтому вы, вероятно, не захотите, чтобы сервер остановил приложение, если можно обойтись без этого. С другой стороны, предположим, что в приложении происходит утечка памяти, и такое избыточное потребление памяти может привести к проблемам в работе других еще более важных приложений на том же самом сервере. В такой ситуации, разумнее было бы остановить приложение до того, как возникнет шанс его пересечения с другим приложением.
Осталась вкладка дополнительно, тут можно явным образом задать какие процессоры использовать и указать правила управления, о них ниже.
Если вы нажмете кнопку перераспределить ресурсы, то сможете добавить дополнительные условия.
Не забудьте еще настроить уведомления о событиях и все ваш Windows System Resource Manager, готов к работе.
Использование Диспетчера системных ресурсов Windows (WSRM) для распределения ресурсов в Windows Server 2008
Одна из главных трудностей при разработке решений любого масштаба — это обеспечение равного доступа. В Windows Server 2008 распределение ресурсов между решениями, имеющими доступ к терминальному серверу Windows (Windows Terminal Server), было значительно усовершенствовано за счет нового компонента. Диспетчер системных ресурсов Windows позволяет распределять оперативную память и ресурсы ЦП на основе политик. Это позволяет сортировать процессы по определенным критериям. Можно, например, связать исполняемые файлы Microsoft Office с соответствующими критериями процессов и выработать определенную политику распределения ресурсов на их основе.
На рис. A показано встроенное приложение WSRM в Windows Server.
WSRM позволяет задавать ограничения на использование ресурсов по определенным схемам, давая администратору возможность самостоятельно решать, как должно вести себя приложение, если ему не хватает оперативной памяти. Можно настроить ограничения таким образом, чтобы по достижении заданного порога приложение отключалось или регистрировалось в журнале событий. Правда, для того, чтобы выявить оптимальное соотношение ресурсов для каждого процесса, придется потрудиться. Кроме того, WSRM позволяет управлять распределением ресурсов по расписанию (в зависимости от степени загруженности в тот или иной день недели), а также создавать глобальные политики для отдельных учетных записей или сеансов.
Есть у WSRM одно ограничение: этот компонент доступен только в версиях Windows Server 2008 Enterprise и Datacenter, которые стоят намного дороже издания Standard. Так что все зависит от того, насколько оправданы такие расходы.
Обратите внимание: WSRM не присутствует в сравнительной таблице компонентов Windows Server 2008 на сайте Microsoft, так что планируйте развертывание с учетом этого фактора.
Windows System Resource Manager Overview
Applies To: Windows Server 2012
You can use Windows System Resource Manager to allocate processor and memory resources to applications, users, Remote Desktop Services sessions, and Internet Information Services (IIS) application pools.
With Windows System Resource Manager for the Windows ServerВ® 2012 operating system, you can manage server processor and memory usage with standard or custom resource policies. Managing your resources can help ensure that all the services provided by a single server are available on an equal basis or that your resources will always be available to high-priority applications, services, or users.
Windows System Resource Manager only manages processor resources when the combined processor load is greater than 70 percent. This means that it does not actively limit the resources that can be used by each consumer when processor load is low. When there is contention for processor resources, resource allocation policies help ensure minimum resource availability based on the management profile that you define.
Role/Feature description
You can use Windows System Resource Manager to:
Manage system resources (processor and memory) with preconfigured policies, or create custom policies that allocate resources per process, per user, per Remote Desktop Services session, or per Internet Information Services (IIS) application pool.
Use calendar rules to apply different policies at different times without manual intervention or reconfiguration.
Automatically select resource policies that are based on server properties and events (such as cluster events or conditions) or changes to installed physical memory or number of processors.
Collect resource usage data locally or in a custom SQL database. Resource usage data from multiple servers can be consolidated on a single computer running Windows System Resource Manager.
Create a computer group to help organize Remote Desktop Session Host servers that you want to manage. Policies can easily be exported or modified for an entire computer group.
Practical applications
Because Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is designed to give as many resources as possible to non-operating system tasks, a server running a single role usually does not require resource management. However, when multiple applications and services are installed on a single server, they are not aware of competing processes. An unmanaged application or service will typically use all available resources to complete a task. Thus, it is important to use a tool such as Windows System Resource Manager to manage system resources on multipurpose servers. Using Windows System Resource Manager provides two key benefits:
More services can run on a single server because service availability can be improved through dynamically managed resources.
High-priority users or system administrators can access the system even during times of maximum resource load.
Methods of resource management
Windows System Resource Manager includes five built-in resource management policies that you can use to quickly implement management. In addition, you can create custom resource management policies to meet your specific needs.
Built-in resource management policies
You can enable built-in resource management policies by selecting the type of policy to use. No further configuration is required.
Equal per process
When the Equal_Per_Process resource allocation policy is managing the system, each running process is given equal treatment. For example, if a server that is running ten processes reaches 70 percent processor utilization, Windows System Resource Manager will limit each process to using 10 percent of the processor resources while they are in contention. Note that resources not used by low utilization processes will be allocated to other processes.
When the Equal_Per_User resource allocation policy is managing the system, processes are grouped according to the user account that is running them, and each of these process groups is given equal treatment. For example, if four users are running processes on the server, each user will be allocated 25 percent of the system resources to complete those processes. A user running a single application is allocated the same resources as a user running several applications. This policy is especially useful for application servers.
Equal per session
When the Equal_Per_Session resource allocation policy is managing the system, resources are allocated on an equal basis for each session connected to the system. This policy is for use with RD Session Host servers.
Equal per IIS application pool
When the Equal_Per_IISAppPool resource allocation policy is managing the system, each running IIS application pool is given equal treatment, and applications that are not in an IIS application pool can only use resources that are not being consumed by IIS application pools.
Weighted Remote Sessions
When the Weighted_Remote_Sessions resource allocation policy is managing the system, the processes are grouped according to the priority assigned with the user account. For example, if three users are remotely connected, the user assigned Premium priority will receive highest priority access to the CPU, the user assigned Standard priority will receive second priority to the CPU, and the user assigned Basic priority will receive lowest priority to the CPU. This policy is for use with RD Session Host servers.
.jpeg) Note Note |
|---|
.jpeg) Note Note |
|---|