- Back up and restore your PC
- Back up
- Create a system image
- Keeping different versions of system images
- Create a restore point
- Restore
- Restore a backup made on another computer
- Find files that were restored from a backup made on another computer
- Restore files from a file backup after restoring your computer from a system image backup
- Recovery options in Windows 10
Back up and restore your PC
To learn how to back up and restore individual files on a Windows-based computer:
To learn how to back up and restore in Windows 10:
Back up
There are several ways to back up your PC.
Select the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
Do one of the following:
If you’ve never used Windows Backup before, or recently upgraded your version of Windows, select Set up backup, and then follow the steps in the wizard.
If you’ve created a backup before, you can wait for your regularly scheduled backup to occur, or you can manually create a new backup by selecting Back up now.
If you’ve created a backup before, but want to make a new, full backup rather than updating the old one, select Create new, full backup, and then follow the steps in the wizard.
Note: Do not back up files to the same hard disk that Windows is installed on. For example, do not back up files to a recovery partition. Always store media used for backups (external hard disks, DVDs, or CDs) in a secure place to prevent unauthorized people from having access to your files; a fireproof location separate from your computer is recommended. You might also consider encrypting the data on your backup.
Create a system image
System images contain all of the info on your PC at a particular state.
Right-click the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
In the left pane, choose Create a system image, and then follow the steps in the wizard. 
Note: To create a system image of a drive, it must be formatted to use the NTFS file system. If you save the system image on a hard drive or USB flash drive, it must be formatted to use the NTFS file system.
Keeping different versions of system images
You can keep several versions of system images. On internal and external hard drives, older system images will be deleted when the drive runs out of space. To help conserve disk space, delete older system images.
If you’re saving your system images in a network location, you can only keep the most current system image for each computer. System images are saved in the format of drive\WindowsImageBackup\computer name\. If you already have a system image for a computer and are creating a new one for the same computer, the new system image will overwrite the old one.
If you want to keep the old system image, you can copy it to a different location before creating the new system image by following these steps.
Navigate to the location of the system image.
Copy the WindowsImageBackup folder to a new location.
Create a restore point
You can use a restore point to restore your computer’s system files to an earlier point in time. Restore points are automatically created each week by System Restore and when your PC detects change, like when you install an app or driver.
Here’s how to create a restore point.
Right-click the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > System.
In the left pane, select System protection.
Select the System Protection tab, and then select Create.
In the System Protection dialog box, type a description, and then select Create.
Restore
Right-click the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
Do one of the following:
To restore your files, choose Restore my files.
To restore the files of all users, choose Restore all users’ files.
Do one of the following:
To look through the contents of the backup, select Browse for files or Browse for folders. When you’re browsing for folders, you won’t be able to see the individual files in a folder. To view individual files, use the Browse for files option.
To search the contents of the backup, select Search, type all or part of a file name, and then select Search.
Tip: If you’re searching for files or folders associated with a specific user account, you can improve search results by typing the location of the file or folder in the Search for box. For example, to search for all JPG files that were backed up, type JPG in the Search for box. To only search for JPG files associated with the user Bill, type C:\Users\Bill\JPG in the Search for box. Use wildcard characters such as *.jpg to search for all JPG files that were backed up.
Restore a backup made on another computer
You can restore files from a backup that was created on another computer running Windows Vista or Windows 7.
Select the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
Choose Select another backup to restore files from, and then follow the steps in the wizard. 
Find files that were restored from a backup made on another computer
If you’re restoring files from a backup that was made on another computer, the files will be restored in a folder under the user name that was used to create the backup. If the user names are different, you’ll need to navigate to the folder where the files are restored. For example, if your user name was Molly on the computer that the backup was made on but your user name is MollyC on the computer that the backup is being restored on, the restored files will be saved in a folder labelled Molly.
To find restored files:
Select the Start button, then select Computer.
Double-click the icon of the drive that the files are saved on, for example C:\.
Double-click the Users folder. You will see a folder for each user account.
Double-click the folder for the user name that was used to create the backup. The restored files will be in the various folders based on where they were located originally.
Restore files from a file backup after restoring your computer from a system image backup
After you restore your computer from a system image backup, there may be newer versions of some of your files in a file backup that you want to restore.
To restore files from a file backup that was created after the system image backup was created, follow these steps.
Select the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
Choose Select another backup to restore files from. 
In Backup Period, select the date range of the backup that contains the files that you want to restore, and then follow the steps in the wizard.
Recovery options in Windows 10
If you’re having problems with your PC, the following table can help you decide which recovery option to use.
See this section
Your PC isn’t working well and you recently installed an update.
Your PC isn’t working well and it’s been a while since you installed an app, driver, or update.
Your PC won’t start, you haven’t created a recovery drive, and resetting your PC didn’t work.
Your PC won’t start and you haven’t created a recovery drive.
Your PC won’t start and you’ve created a recovery drive.
You want to reinstall your previous operating system.
Your PC isn’t working well and you recently installed an app.
Click one of the recovery options below and follow the steps to try to get things working again.
If you’ve recently installed a Windows update, uninstall the update to try to resolve the issue.
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > View your update history > Uninstall updates.
View update history settings
Right-click the update you want to remove, and then select Uninstall.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
Resetting reinstalls Windows 10, but lets you choose whether to keep your files or remove them, and then reinstalls Windows. You can reset your PC from Settings, the sign-in screen, or by using a recovery drive or installation media.
Reset your PC from Settings
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery .
Open Recovery settings
Under Reset this PC, select Get started and then choose from the options and/or settings in the table below.
Keep my files > Change settings > Preinstalled apps On
Reinstalls Windows 10 and keeps your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Restores any apps your PC manufacturer installed if your PC came with Windows 10.
Keep my files > Change settings > Preinstalled apps Off
Reinstalls Windows 10 and keeps your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Removes any apps your PC manufacturer installed.
Reinstalls Windows 10 and removes your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Removes any apps your PC manufacturer installed. (If your PC came with Windows 10, apps from your PC manufacturer will be reinstalled.)
Note: Remove everything > Change settings gives you two options.
Data erasure On removes files and cleans the drive. If you’re planning to donate, recycle, or sell your PC, use this option. This might take an hour or two, but it makes it harder for other people to recover files you’ve removed.
Data erasure Off just removes files. It takes less time, but is less secure.
Reset your PC from the sign-in screen
If you can’t open Settings, you can reset your PC from the sign-in screen. Here’s how:
Press Windows logo key + L to get to the sign-in screen, and then restart your PC by pressing the Shift key while you select the Power button > Restart in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Your PC will restart in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) environment.
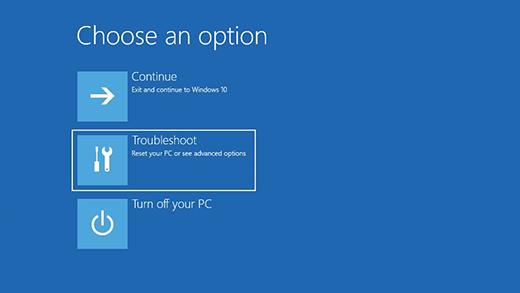
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Reset this PC, and then choose one of the options in the previous table.
Connect the installation media you created to your PC and reinstall Windows 10.
Open File Explorer and select the drive with the installation media.
From the root directory of the drive, double-click setup.exe, and then select Yes when asked if you’d like to allow the app to make changes to your device.
Select Change what to keep.
Select one of the following options, and then select Next:
Keep personal files and apps – This will preserve your personal data, apps, and settings.
Keep personal files only – This will preserve your personal data and settings, but all your apps will be removed.
Keep nothing – This will remove all personal data, settings, and apps.
Warning: You cannot undo a reinstallation of Windows 10. Be sure to back up your files first if you choose the Keep nothing option.
To finish, select Install to start reinstalling Windows 10 on your PC.
Your PC will restart several times during the resinstallation.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to use a recovery drive to restore or reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
If your PC won’t start and you haven’t created a recovery drive, download installation media and use it to restore from a system restore point or reset your PC.
Download the Windows 10 media creation tool and then run it.
Select Create installation media for another PC.
Choose a language, edition, and architecture (64-bit or 32-bit).
Follow the steps to create installation media, and then select Finish.
Connect the installation media you created to your nonfunctional PC, and then turn it on.
On the initial setup screen, enter your language and other preferences, and then select Next. If you don’t see the setup screen, your PC might not be set up to boot from a drive. Check your PC manufacturer’s website for info on how to change your PC’s boot order, and then try again.
Select Repair your computer.
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot. From there, you can:
Restore from a system restore point by selecting Advanced options > System Restore. This will remove recently installed apps, drivers, and updates that might be causing your PC problems. Restoring from a restore point won’t affect your personal files.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to use a recovery drive to restore or reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
If your PC won’t start, you can use a recovery drive to restore from a system restore point or recover your PC. For info on how to create a recovery drive on a working PC, see Create a recovery drive.
Note: If you are using a Surface, see Creating and using a USB recovery drive for Surface to download and create a USB recovery image specifically for your Surface device.
To restore or recover using the recovery drive:
Connect the recovery drive and turn on your PC.
Press Windows logo key + L to get to the sign-in screen, and then restart your PC by pressing the Shift key while you select the Power button> Restart in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Your PC will restart in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) environment.
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot, and then select one of the following two options. (If you don’t see the Choose your option screen, your PC might not be set up to boot from a drive. Check your PC manufacturer’s website for info on how to change your PC’s boot order.)
To restore from a system restore point, select Advanced Options > System Restore. This won’t affect your personal files, but it will remove recently installed apps, drivers, and updates that might be causing your PC problems.
To reinstall Windows 10, select Advanced Options > Recover from a drive. This will remove your personal files, apps and drivers you installed, and changes you made to settings.
For a limited time after upgrading to Windows 10, you’ll be able to go back to your previous version of Windows by selecting the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery and then selecting Get started under Go back to the previous version of Windows 10. This will keep your personal files, but it’ll remove apps and drivers installed after the upgrade, as well as any changes you made to settings. In most cases, you’ll have 10 days to go back.
Open Recovery settings
To go back, you’ll need to:
Keep everything in the windows.old and $windows.
bt folders after the upgrade.
Remove any user accounts you added after the upgrade.
Know the password you used to sign in to Windows 7 or Windows 8.1 (if you used one).
Have the USB drive you used to upgrade to Windows 10 (if you used one).
Note: If you go back to Windows 8.1, some apps that came with Windows, like Mail and People, might not work anymore. To fix the apps, reinstall them from the Microsoft Store.
Note: The option in Settings to go back to your previous version of Windows is only available for a limited time after upgrading.
Info for Windows Insiders
If you’re an Insider and the current preview build isn’t working for you, select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery . Under Go back to the previous version of Windows 10, select Get Started. This won’t remove your personal files, but it’ll remove recently installed apps and drivers, and change settings back to their defaults.
Going back to an earlier build won’t remove you from the Insider Program. When the next preview build is ready, it’ll be installed on your PC.
This option takes your PC back to an earlier point in time, called a system restore point. Restore points are generated when you install a new app or driver, and when you create a restore point manually. Restoring won’t affect your personal files, but it will remove apps, drivers, and updates installed after the restore point was made.
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel,andthen choose it from the list of results
In the Control Panel search box, type recovery.
Select Recovery > Open System Restore.
In the Restore system files and setting box, select Next.
Select the restore point that you want to use in the list of results, and then select Scan for affected programs.
If you don’t see the restore point that you want to use, select the Show more restore points check box to see more restore points.
If you’re not seeing any restore points, it might be because system protection isn’t turned on. Here’s how to check:
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel,andthen choose it from the list of results.
In the Control Panel search box, type recovery.
Select Recovery > Configure System Restore > Configure and see if the Turn on system protection option is selected.
If the Turn on system protection option is not selected, system protection isn’t turned on and there aren’t any restore points. In this scenario, you won’t be able to recovery your PC using a system restore point and will need to use one of the other recovery options listed on this page.
If the Turn on system protection option is selected, continue with step 6.
You’ll see a list of items that will be deleted if you remove this restore point. If you’re OK with the deletions, select Close> Next > Finish.