- How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
- How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
- Opening Task Manager
- Understanding the Processes tab
- Identifying processes with high-resource usage
- Stopping processes with high-resource usage
- Wrapping things up
- More Windows 10 resources
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
- Обзор приложения Task Manager
- Task Manager — что это
- Почему грузит процессор
- Как отключить Task Manager
- 11 ways to manage running processes with the Task Manager in Windows 10
- What is the Processes tab and how to access it?
- 1. How to add or remove data columns in Task Manager’s Processes tab
- 2. How to sort running apps and processes in Task Manager’s Processes tab
- 3. How to change the way data values are displayed in the Processes tab
- 4. How to expand and collapse running processes in the Task Manager
- 5. How to end running processes using the Task Manager
- 6. How to provide feedback on a running process to Microsoft
- 7. How to create a dump file for a running process using the Task Manager
- 8. How to see details for a running process in the Task Manager
- 9. How to find the location of a running process in the Task Manager
- 10. How to research an unknown process or app using the Task Manager
- 11. How to view the properties of a running app from the Task Manager
- How crowded is your Task Manager’s Processes tab?
How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
The Task Manager is an advanced tool that comes with Windows 10, and it provides a number of tabs that allow you to monitor the applications, processes and services running on your computer. However, you’ll likely find yourself using the Processes tab more than anything else, because it lets you quickly see how system resources are utilized, which can be very helpful when trying to troubleshoot applications or find out why your computer is suddenly slow.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to use Task Manager to identify and stop processes that use excessive system resources, to keep your computer at top speeds.
How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
Opening Task Manager
If you want to use Task Manager to view and stop processes with high-resource usage, you first need to know how to open the tool. Here are a few ways to open Task Manager:
- Right-click the Taskbar and click on Task Manager.
- Open Start, do a search for Task Manager and click the result.
- Use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut.
- Use the Ctrl + Alt + Del keyboard shortcut and click on Task Manager.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the power-user menu and click on Task Manager.
If this is your first time opening Task Manager, the tool will probably open in compact mode, which only lists running applications. Click the More details button to access Task Manager in advanced mode.

Understanding the Processes tab
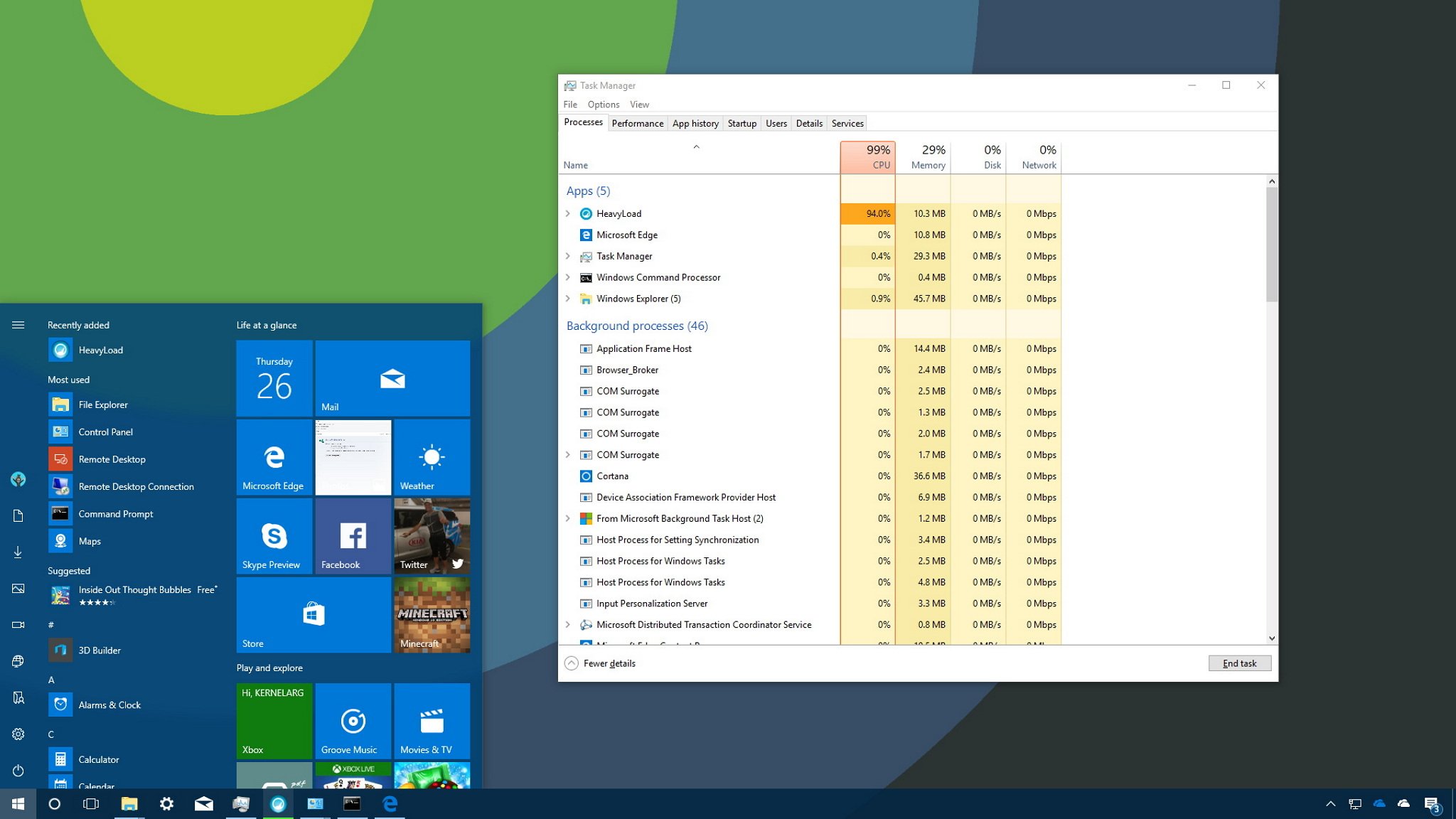
When you’re in advanced mode, you’ll see a number of tabs, including «Performance», «App history», «Startup», «Users», «Details», «Services», and the one we’re interested in, the «Processes» tab. Typically, the Processes tab is the first place you want to go to detemine which process is draining your computer’s resources. This tab lists all the running processes in a single view grouped by «Apps», «Background processes» and «Windows Processes». On Windows 10, you can also find multiple instances or other processes under the same process, which helps you to better understand how they’re organized and how they use system resources.
You can always expand a group to see all the processes by clicking the chevron-right icon or by right-clicking the item and selecting Expand. Usually, you’ll see groups for Windows processes when opening multiple tabs on your web browser or multiple File Explorer windows, for example.
Identifying processes with high-resource usage
If an application is not responding, a website is taking a long time to load, or your system fan starts getting loud, you can quickly use Task Manager to troubleshoot the problem. In the Processes tab, the first thing you want to look at is the percentage of the total resource use for the processor, memory, hard drive and network. You can click the column names to sort the list and bring to the top the ones using the most resources. If you see any of these resources running high (90 percent or higher), you might have found the problem.
Task Manager also uses colors to highlight processes that use the most resources. You’ll notice that as a process starts to consume more resources, the color begins to change from a light- to a dark-shade of orange, making it easier to tell which one is causing the problem.
Typically, when you’re not actively using applications and your computer isn’t working on anything specific, such as maintenance, your total CPU usage should be less than 30 percent. Applications that are running, even if you’re not using them, and processes use part of your computer’s memory, and that usage will increase as you use or launch more applications. Memory usually won’t be an issue unless you run out of it, in which case your computer will start using virtual memory, and that can cause your PC to slow down. Generally speaking, depending on your system configuration, your total memory usage should be below 60 percent. If you’re not copying files or rendering videos, disk usage should be below 5 percent.
Network connectivity is almost never the reason your system is slow, but there could be a problem in the network causing web content to take a long time to load. If you’re having problems downloading files, and you see «Network» stuck at 0 percent, you may have an idea of what’s going on.
Stopping processes with high-resource usage
After you identify the problem, right-click the process, and select End task to terminate it. Alternatively, you can simply select the item and click the End task button in the bottom-right corner.
While stopping a process using the Task Manager will most likely stabilize your computer, ending a process can completely close an application or crash your computer, and you could lose any unsaved data. It’s always recommended to save your data before killing a process, if possible.
If you’re not sure about how the process you’re trying to terminate affects your PC, you can right-click it, and select the Search online option. This action opens your web browser and displays a search result with more information about the process. Windows 10 is also smart enough to let you know if you’re about to end an essential system process that can crash your computer.
Wrapping things up
Although there are many other ways to troubleshoot system performance, Task Manager gives you an easy way to find out at a glance why your computer is slow or if an app is not responding, and then quickly act on it. You can end an application that isn’t responding using Task Manager in compact mode, but the advanced view gives you more information about processes that are acting up in Windows 10.
More Windows 10 resources
For more help articles, coverage, and answers to common Windows 10 questions, visit the following resources:
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
In this guide, we’ll show you the steps to get rid of the update KB5001330 to fix profile, gaming, and BSoD problems with the Windows 10 October 2020 Update and May 2020 Update.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!
Обзор приложения Task Manager
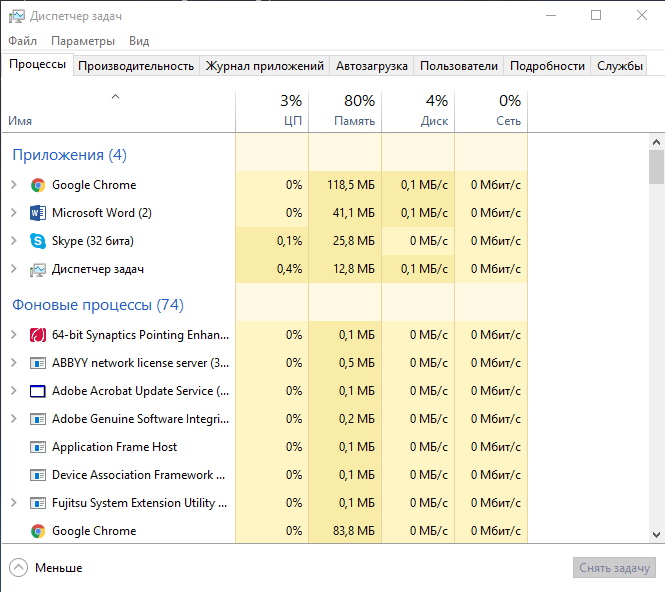
При первых признаках снижения производительности компьютера пользователи запускают «Диспетчер задач», дабы выяснить виновника подвисаний и предпринять соответствующие меры. Ирония заключается в том, что проблемным процессом может оказаться именно «Диспетчер задач». Давайте узнаем ответ на два самых главных вопроса: Task Manager Windows 10 что это и как остановить?
Task Manager — что это
Task Manager – это стандартное приложение в Windows, отвечающее за мониторинг и контроль запущенных процессов и служб. С его помощью можно определить степень нагрузки на аппаратную составляющую каждого модуля системы и запущенного приложения. К основным функциям можно отнести:
- запуск и завершение процессов;
- приостановка работы служб и изменение их параметров автозапуска;
- редактирование модуля автозагрузки;
- отладка запущенных приложений;
- смена активных пользователей.
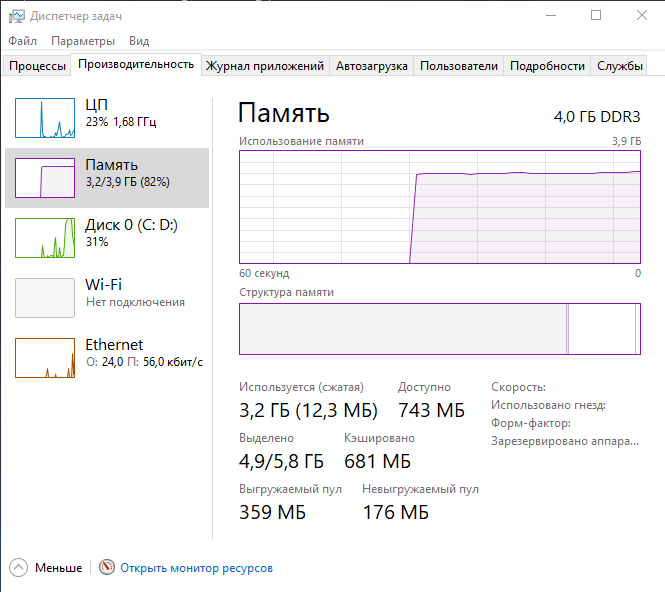
Почему грузит процессор
С помощью этой утилиты можно завершить процесс зависшей программы, не прибегая к перезагрузке компьютера. Поэтому существует две основные версии возникновения проблем с Task Manager:
- Заражение вредоносными программами. Если у вас стоит лицензионная версия Windows, единственной причиной остается проникновение в систему вируса, повреждающего Task Manager или маскирующегося под него.
- Пиратская версия Windows. Все сборки нелицензионных версий ОС делаются вручную. Поэтому вероятность повреждения какого-либо компонента системы довольно велика.
Как отключить Task Manager
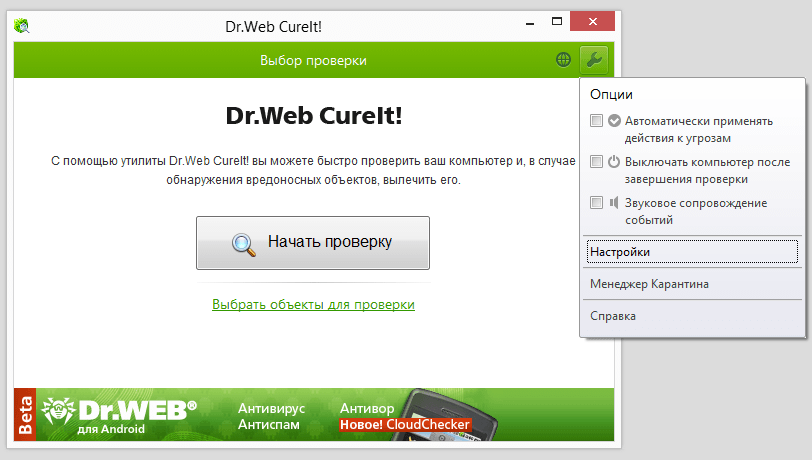
Исходя из первой проблемы, очевидное решение — глубокое сканирование памяти компьютера с последующим лечением или удалением зараженных файлов. Для этого:
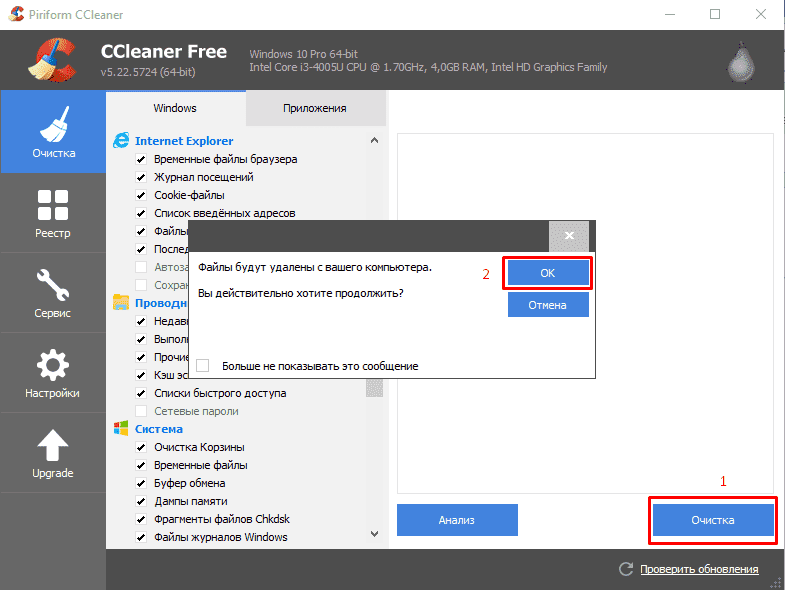
- Скачайте антивирус Dr.Web CureIt! с официального сайта и выполните глубокое сканирование памяти жесткого диска и ОЗУ.
- После окончания процедуры следуйте подсказкам утилиты по дальнейшему лечению или удалению объектов.
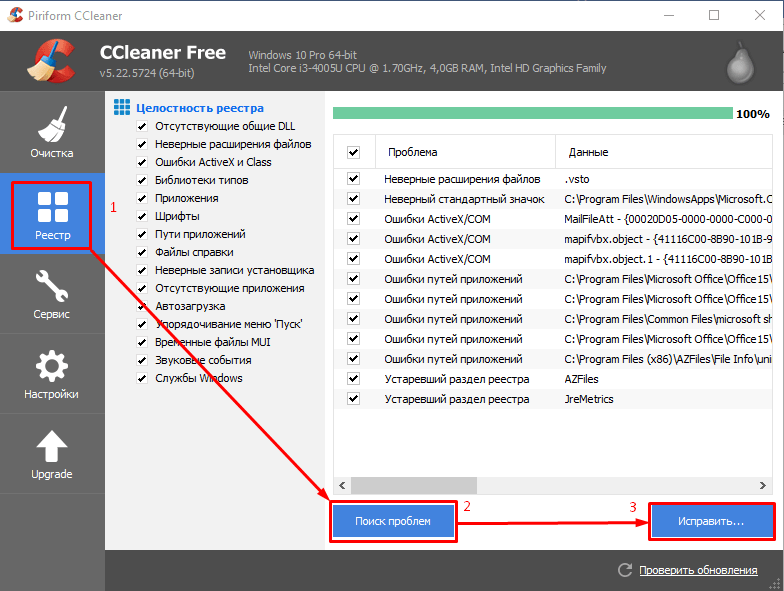
- Загрузите и установите CCleaner.
- Очистите ПК от временных файлов и старых логов.
- Удалите пустые и устаревшие ключи реестра.
- Перезагрузите компьютер.
Если ничего не помогло и версия ОС у вас не оригинальная – единственным выходом является переустановка системы на лицензионную.
Теперь вы знаете, что это за процесс Task Manager и как его оптимизировать. Для предотвращения подобных ситуаций в будущем настоятельно рекомендуется пользоваться оригинальным программным обеспечением последней версии. Со всеми вопросами жду в комментариях!
11 ways to manage running processes with the Task Manager in Windows 10
The Windows 10 Task Manager gives you a lot of power when it comes to monitoring system resources. The Processes tab shares more information than ever before, allowing you to customize the data it shows according to your needs. Here is how to tweak the Task Manager’s Processes tab in Windows 10 and become more efficient, by ensuring the data relevant to you is displayed in a way that suits your needs better than the default view:
What is the Processes tab and how to access it?
The Processes tab lists all the apps, background processes, and Windows processes running at any given time, providing useful data about each of them. It is available in the full version of the Task Manager. There are several options available to open the Task Manager, but we think the most comfortable is the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + Shift + Esc.“ If you skipped Windows 8, and if this is your first time accessing the tool, it opens in what we call the compact view, showing you a list of all the apps currently running on your Windows 10 device. To open the full version of the Task Manager, click or tap More details at the bottom of the compact view.
The full version of the Task Manager opens, and the Processes tab is the default tab.
TIP: The Task Manager can be customized to open in any tab you want. To find out more, read How to set the default view/tab for the Windows 10 Task Manager.
1. How to add or remove data columns in Task Manager’s Processes tab
In the Processes tab, you get information on every app, background process, and Windows process currently running on your computer. This data is structured and displayed in columns. Click or tap on a column’s header, and drag it to reorder the columns in the order you prefer. You can pick and choose the information shown in the Processes tab by adding and removing columns. Right-click or press-and-hold on an existing column’s header and select which of the fourteen optional columns are displayed in the Processes tab of the Task Manager. Keep in mind that the Name column is the only column that you cannot hide.
To ensure that the columns you select provide you with relevant data, here is a run-down of what they have to offer:
Type – Displays whether the process is an app, a background process, or a Windows process. If “Group by type” is selected, this column becomes redundant
Status – Displays whether or not a process is suspended. When something is suspended, it is running in the background, but it has no access to CPU cycles and uses little memory.
PID – Displays a unique Process Identifier for each running process. These numbers can be used to match a running process with an error or event that lists the PID.
Process name – Displays the name of the process’s executable. E.g., 7zFM.exe for 7-Zip File Manager.
Command line – Displays the command-line syntax run for each process. This lets you see if any apps or processes have been launched with special command-line parameters and also gives you the location of each process’s executable file.
CPU – Shows each process’s processor usage.
Memory – Shows each process’s RAM usage.
Disk – Shows each process’s hard disk usage.
Network – Shows each process’s network usage.
GPU – Shows each process’s usage of the video card.
GPU engine – Shares which GPU engine is utilized by each process. According to Microsoft: a GPU engine represents an independent unit of silicon on the graphics card, that can be scheduled and can operate in parallel with another. You can find our more about this concept, here.
Power usage – Displays the power used by each process.
Power usage trend – Shows the overall trend in power usage for each process.
2. How to sort running apps and processes in Task Manager’s Processes tab
By default, the Task Manager’s Processes list is sorted logically by process type. This means that all apps, background processes, and Windows 10 processes are grouped together and sorted within their group in this first column of the tab, called Name. While we are big fans of this system, you may wish to sort the list alphabetically instead. Click or tap View and deselect “Group by type” if you want all the active apps and processes to be displayed in an alphabetical list.
Clicking or tapping on a column’s header allows you to sort the running apps and processes based on the values displayed in that column. E.g., clicking on Memory sorts the list by how much RAM the processes are using. This can come in handy if you are wondering what processes consume the most or the least resources on your computer. Regardless of the sorting method you are using, select the “Group by type” option in the View menu if you wish to return to the default sorting at any point.
3. How to change the way data values are displayed in the Processes tab
On top of allowing you to customize which information is shown, the Processes tab also lets you decide how some of that data is displayed. For the Memory, Disk and Network columns you can choose whether to display the data using values – MB of memory, MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage – or as a percentage of the total available resource. Right-click or press-and-hold on any column’s header or process in the Processes tab of theTask Manager, and go to Resource values. Choose one of the resources and then select either Percents or Values to have the data displayed according to your needs and preferences.
4. How to expand and collapse running processes in the Task Manager
Some processes are more complex than others, involving more than just the main process. The Task Manager’s Processes tab allows you to expand listed processes and get more details about the subprocesses running under them. The number of subprocesses is indicated by a number in brackets following each process. To expand a single process, right-click or press-and-hold on it, and click or tap Expand. An easier way to do this is by clicking or tapping the arrow to the left of the process.
You can click the arrow again, or you can right-click or press-and-hold on that process, and go to Collapse if you want to hide the subprocesses again.
You can also expand any collapsed entries by clicking or tapping View and then Expand all.
To instantly collapse all expanded entries, click or tap Collapse all from the View menu.
TIP: For multi-process applications, the contextual menu displays greyed out options when right-clicking or pressing-and-holding the main (parent) process. Right-click or press-and-hold on each subprocess to interact with it.
5. How to end running processes using the Task Manager
The primary use of the Task Manager is to close running processes that are no longer responding. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process and a contextual menu opens. Click or tap End task to close the process.
You can also select the app and click or tap the End task button on the bottom-right corner of the Processes tab to close the process.
6. How to provide feedback on a running process to Microsoft
The Feedback Hub is easily accessible from the Task Manager, allowing you to offer feedback on a running process. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then choose to Provide feedback.
When the Feedback Hub opens, you can sign in with your Microsoft account and use it to send your issue, criticism, or suggestion to Microsoft.
7. How to create a dump file for a running process using the Task Manager
A dump file is a large file that uses the DMP format and provides details on what a particular process or application is doing at the exact time the dump file is created. This usually comes in handy to software developers trying to solve a bug or a problem with that process. To create a dump file, right-click or press-and-hold on any process and click or tap “Create dump file.”
8. How to see details for a running process in the Task Manager
The Details tab of the Task Manager unsurprisingly provides precise details about running processes. However, this tab’s sorting options are limited, so finding more about a certain process can turn into a bit of a treasure hunt, especially if you have many processes running on your computer. Luckily, the Processes tab makes up for that by providing an option to highlight the corresponding process in the Details tab. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then click or tap “Go to details.“
The focus moves to the Details tab, where the corresponding executable file is highlighted.
9. How to find the location of a running process in the Task Manager
Finding the exact location on your hard drive of the executable file corresponding to an app or a process is also made easier with the Task Manager. Right-click or press-and-hold on the process in the Processes tab and click or tap on “Open file location.”
The File Explorer opens at the folder where your application’s executable file is stored. The corresponding file is selected when the folder opens.
10. How to research an unknown process or app using the Task Manager
Not only does the Task Manager’s Processes tab show apps that are currently open, but it also displays background processes, which are mostly of interest to more advanced users. To research an unknown app or process, right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Processes tab, and then click or tap Search online.
In a new tab, your default web browser runs a web search with the name of the process’s or app’s executable file on Bing (regardless of your default search engine), helping you get more information.
11. How to view the properties of a running app from the Task Manager
The properties of a process or an application offer a lot of information about the executable that runs it. They show the file’s size, location, access dates, and security settings, and let you troubleshoot compatibility issues. Right-click or press-and-hold on an app or process from the Processes list of the Task Manager and choose Properties.
The Properties window opens, providing you access to useful information about the app.
How crowded is your Task Manager’s Processes tab?
Since we went over the different ways you can customize this tab, let us know what you choose to see in your Task Manager. Do you keep it basic like the majority of users or prefer a more detailed view? Comment below and let’s discuss.