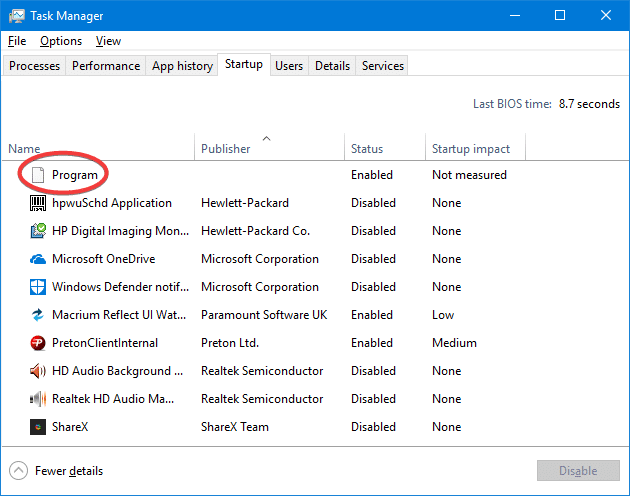
What is “Program” in Task Manager Startup Tab
When you open Task Manager and click on the Startup tab to manage auto-start entries, you may notice one or more entries showing up as “Program” showing up with a blank or generic icon and without any Publisher information.
The unknown “Program” entries are most likely caused if both of the following conditions are true:
- The startup entry refers to an invalid or non-existent file under “Program Files” folder.
- The registry value data corresponding to that startup entry is not enclosed within double-quotes.
This article tells what does the “Program” entries in the Startup tab mean and how to get rid of those entries.
What is “Program” in Task Manager Startup Tab
To identify and fix the unknown “Program” entries in the Startup tab of Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Start Task Manager ( Ctrl + Shift + Esc ), and select the Startup tab
- Right-click on the column header and enable these two options: Startup type and Command line
Now the origin of the “Program” entries are displayed. You can now see the full path and command-line of that startup entry.
Fix 1: If the program (.exe) file is NOT present in the specified folder, then see article Remove invalid entries from Task Manager Startup tab to know how to remove the orphaned Startup entry in Task Manager via the Registry Editor or using the Autoruns utility from Microsoft.
In one example, the entry Realtek was causing the problem. The registry Run key had this entry:
The application had long back been uninstalled but the orphaned Startup entry remains.
The Startup entry could be located in any one of the following registry locations.
Note that the “Disabled” startup entries in Task Manager are stored in this part of the registry:
Fix 2: If the program (.exe) file is present in the specified folder (less likely):
- Start the Registry Editor ( regedit.exe ) and go to each of the Run registry keys mentioned above.
- Locate the corresponding startup entry, double-click on it and add double-quotes around the file path.
- Exit the Registry Editor.Now, the Startup item shows up as below:
If the Publisher info is missing and the entry shows up as a generic icon as in the above screenshot, then the program is most likely missing. In that case, you may delete the orphaned Startup entry using the steps listed in Remove invalid entries from Task Manager Startup tab.
That’s it! You’ve now fixed/eliminated the suspicious “Program” entry from Task Manager Startup tab.
What is the Program program showing up in Windows 8 Task Manager Startup tab?
Replies (67)
* Please try a lower page number.
* Please enter only numbers.
* Please try a lower page number.
* Please enter only numbers.
Some programs, particularly system maker’s included programs, do not identify
themselves by name in the StartUp tab.
If you Right Click on any of the existing Column Names at the top of the columns in the
StartUp tab there are other column display choices. Select «Command Line» and you can
see what program is opening.
You can use AutoRuns again and check the command line and the file name with those
programs running in Task Manager’s — StartUp tab — Command line column.
Note using Win Key + X and Win Key + W (to get to Control Panel, Run, and Settings
as needed). Win Key + D calls the desktop and the using Win Key toggles Desktop and
Start Screen.
How to perform a clean boot to troubleshoot a problem in Windows Vista, Windows 7,
or Windows 8/8.1
Other programs to help :
Autoruns — Free — See what programs are configured to startup automatically
when your system boots and you login. Autoruns also shows you the full list
of Registry and file locations where applications can configure auto-start settings.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb963902.aspx
Process Explorer — Free — Find out what files, registry keys and other objects
processes have open, which DLLs they have loaded, and more. This uniquely
powerful utility will even show you who owns each process.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896653.aspx
Hope this helps.
Rob Brown — Microsoft MVP Rob Brown — past Microsoft MVP — Windows Insider MVP 2016 — 2021
Microsoft MVP Windows and Devices for IT 2009 — 2020
Windows task manager applications tab
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Windows Task Manager is a program that comes with Windows and displays information about the processes running and the resources being utilized on your computer. This utility allows you get a good overview of the tasks your computer is performing and the amount of resources each task is utilizing. Using this information you can tune your computer to run optimally and efficiently by disabling programs that may be using too many resources and thus slowing down your computer.
The Windows Task Manager program is broken up into multiple tabs. Each tab is associated with a particular category such as the running applications, running processes, Windows services, the computer’s performance, network utilization, and the users that are currently logged in. This tutorial will discuss how to start the Windows Task Manager and provide information about each category of the Windows Task Manager.
Please note, that tutorial only applies to Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7. As the Task Manager has changed in Windows 8, a separate tutorial will be created for that version of Windows.
How to start the Windows Task Manager and an overview of its interface
The Windows Task Manager can be started by using two methods. The first, and easiest method, is to simply right click on the time shown in your Windows taskbar. When you right click the time, you will be shown a dialog box similar to the one below:
Simply left click on the Task Manager option and the Windows Task Manager will open.
The second method to start the Windows Task Manager is to click on the Start button and type in taskmgr.exe and press the Enter on your keyboard. If you are using Windows XP, then you will need to click on the Run option before typing taskmgr.exe. Once you press Enter on your keyboard, the program will start.
When the Windows Task Manager opens, it will open to the last tab that you viewed before you closed it in the past. If this is the first time you have run the program, then the Task Manager will start in the Applications tab as shown below.
The information displayed by the Windows Task Manager is broken up into different categories. These categories can be accessed by clicking on the particular tab that is associated with them. More information about each category is provided in the sections below.
Finally, Task Manager displays basic information at the bottom of the windows labeled Processes, CPU Usage, and Physical Memory. The Processes number is the amount of processes currently running on the computer, the CPU Usage is the percent of the total CPU processing power that is currently being used, and the Physical Memory percentage is the percentage of total memory currently being used by your running programs and Windows.
Applications Tab
The Applications tab will show you all running programs that can be interacted with by the currently logged in user. That means that you will only see applications that have been started by the user you are currently logged in as. If there are other applications running that were launched by another user, you will not see these applications listed.
The Applications Tab
There is not much information provided on this tab other than the name of the application that is running and its state. Some application states that you may see are Running and Not Responding. Running means that the application is running normally, while Not Responding means that the program is frozen or having an issue.
To close a Not Responding program, you click left click once on the application name so that it is highlighted and then click on the End Task button. This will cause Windows to attempt to terminate the program. If the program is not terminated after you click on the End Task button, you should wait a minute and click on the End Task button again. If that does not work you can try terminating the program through the Processes tab that is discussed in the next section.
Processes Tab
The Processes tab displays a list of all the running processes that are on the computer. Unlike the Applications tab, this tab has the ability to display all programs that are running even if they were started by another user or the operating system itself. When you start Windows Task Manager and go to the Processes tab, by default it will only show the processes for the currently logged in user and some basic operating system processes. An example of this limited view can be seen in the image below.
The Processes for the current user
If you click on the Show processes from all users button, Windows Task Manager will be restarted with Administrative privileges that will allow you to see all processes currently started on the computer. An example of what this looks like can be seen in the image below. Notice how there are much more processes now listed.
Processes tab showing all processes
The standard information that is shown in this tab includes the image name, or file name, the name of the user that launched the process, the amount of CPU power that the process is currently using, how much memory it is using, and a description that is found within the process. It should be noted that not all processes will contain a description, which will cause the description field to be blank. It is also possible to add other columns of information by clicking on the View tab and then selecting Select columns. This will open a screen where you can enable other columns of information for each process.
It is also possible to get more detailed information about the particular process by right-clicking on the process and selecting properties. This will allow you to see the digital signatures of a process, where it is located, and other information.
One of the most common tasks that people use this tab for is to terminate a particular process that may be causing problems on the computer. Whether it is because the program is not responding or it is suspected that the process is related to malware, you can terminate a process by left-clicking on it once so it is selected and then clicking on the End Process tab. You will then be presented with a dialog box asking if you are sure you wish to terminate the process.
Services Tab
The Services tab is only available in Windows Vista and Windows 7. This tab will show you all the Windows Services currently configured in Windows. A Windows Service is a special type of program that is started by Windows when it starts or as necessary and runs in the background performing a particular task. Windows Services are an integral part of the operating system and if they are not running or have been deleted they can cause serious problems with the proper operation of Windows.
The Services Tab
This tab displays information about each service, whether they are running or not, and the service’s description. You can also start and stop an individual service by right-clicking on a service and selecting Stop or Start.
For more details about the services on your machine, you can click on the Services. button to open the Services control panel.
Performance Tab
The Performance tab allows you to see the current and historical CPU and memory utilization on your computer. This tab is useful if you are trying to diagnose why your computer or an application is running slower than normal.
The Performance Tab
The CPU Usage and CPU Usage History boxes show how much CPU processing power your computer is currently using and has been using over time. The Memory and Physical Memory Usage History boxes display the amount of memory that is being used and how much has been used over time. As you can imagine, this information is very useful in determining why your computer may be running slow. For example, if you find your computer is slow and find that the CPU utilization is at 100%, then you know the slow down could be caused by a process using up to much CPU power. You can then go to the Processes tab to see which process may be using up all the CPU power and close it. If you find that there is no particular CPU causing a problem, then this just may be a indication that it is time to upgrade your CPU.
The same diagnostics can be used with memory. Many people do not realize that memory is a vital component of fast computer. If your applications are using up all of your memory than Windows will start writing pieces of memory to a file a on your disk drive. This process is called paging and when it occurs your computer slows down significantly. By using the Performance and Processes tab of the Task Manager, you can quickly determine if a lack of memory is causing your computer to perform more slowly.
Networking Tab
The Networking tab allows you to have a general idea of how much traffic is flowing over a particular network interface on your computer. At the bottom of this screen you will see a list of all the network interfaces on your computer. Above that you will see graphs for each interface that show the network traffic flowing over them.
The Networking Tab
This information can be useful if you are wondering why your Internet or network connection may be to slow. For example, if you see that your network interface is at 100% utilization then something in Windows is using up all of the available bandwidth. You can then determine what program is using the network connection and close it.
Users Tab
The Users tab will display all the users that are currently logged in. An example of what this screen looks like is below.
The Users Tab
From this screen you can Disconnect or Logoff users. If you choose to Disconnect a user, it will terminate that users connection to the computer, but not necessarily log them off. That means that their programs will continue to run on the computer. On the other hand, if you select Logoff, then all of the user’s running programs will be closed and the user will logged off of the computer.
Advanced Task Manager Information
It is not uncommon for a system administrator, or even malware, to disable the Windows Task Manager by changing a setting in the Windows Registry. When the program is disabled, the Task Manager option will be greyed out when you right-click on the taskbar and if you attempt to run the program manually by opening taskmgr.exe, you will receive a message stating «Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator.».
The Task Manager is disabled by creating the following Registry value:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System «DisableTaskMgr» = 1
When the DisableTaskMgr value is set to 1, Windows will not allow you to launch the Task Manager. To enable the Task Manager, you can simply change that value to 0. As making changes in the Registry can be dangerous, it is suggested that you instead download the following registry file if you find that the Task Manager is disabled.
Simply download the above registry file and save it on your desktop. Once it is downloaded, you can double-click on the file and when it prompts you to merge the data, please allow it to do so. Once that data has been merged you will be able to launch the Windows Task Manager again.
Users who read this also read:
How to close a program in Windows
When using Windows there may come a time where you will need to close a program or process that is not responding or that you are concerned is a computer infection. This tutorial will walk you through using the Windows Task Manager to close a program when you cannot close it normally.
How to shut down or restart Windows
It is important to know how to properly shut down or restart your computer so that you do not lose data or corrupt important Windows files or Registry locations. Many people think that you shut down your computer simply by pressing the power button. On some configurations, this will work as Windows will recognize that you press the power button and shut it down gracefully. On the other hand, if .
How to remove a Trojan, Virus, Worm, or other Malware
If you use a computer, read the newspaper, or watch the news, you will know about computer viruses or other malware. These are those malicious programs that once they infect your machine will start causing havoc on your computer. What many people do not know is that there are many different types of infections that are categorized in the general category of Malware.
How to determine what services are running under a SVCHOST.EXE process
A very common question we see here at Bleeping Computer involves people concerned that there are too many SVCHOST.EXE processes running on their computer. The confusion typically stems from a lack of knowledge about SVCHOST.EXE, its purpose, and Windows services in general. This tutorial will clear up this confusion and provide information as to what these processes are and how to find out more .
How to use the Windows Recycle Bin
When you delete a file in Windows it is usually not permanently deleted. Instead, Windows moves the file to a special location called the Recycle Bin. First implemented in Windows 95, the Recycle Bin is a special directory where deleted files are stored in the event that you need to recover them. Sometimes the Recycle Bin is referred to as the trash, trashcan, or garbage. As a computer user, use .