- How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
- How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
- Opening Task Manager
- Understanding the Processes tab
- Identifying processes with high-resource usage
- Stopping processes with high-resource usage
- Wrapping things up
- More Windows 10 resources
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
- tasklist tasklist
- Синтаксис Syntax
- Параметры Parameters
- Имена фильтров, операторы и значения Filter names, operators, and values
- Примеры Examples
How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
The Task Manager is an advanced tool that comes with Windows 10, and it provides a number of tabs that allow you to monitor the applications, processes and services running on your computer. However, you’ll likely find yourself using the Processes tab more than anything else, because it lets you quickly see how system resources are utilized, which can be very helpful when trying to troubleshoot applications or find out why your computer is suddenly slow.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to use Task Manager to identify and stop processes that use excessive system resources, to keep your computer at top speeds.
How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
Opening Task Manager
If you want to use Task Manager to view and stop processes with high-resource usage, you first need to know how to open the tool. Here are a few ways to open Task Manager:
- Right-click the Taskbar and click on Task Manager.
- Open Start, do a search for Task Manager and click the result.
- Use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut.
- Use the Ctrl + Alt + Del keyboard shortcut and click on Task Manager.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the power-user menu and click on Task Manager.
If this is your first time opening Task Manager, the tool will probably open in compact mode, which only lists running applications. Click the More details button to access Task Manager in advanced mode.

Understanding the Processes tab
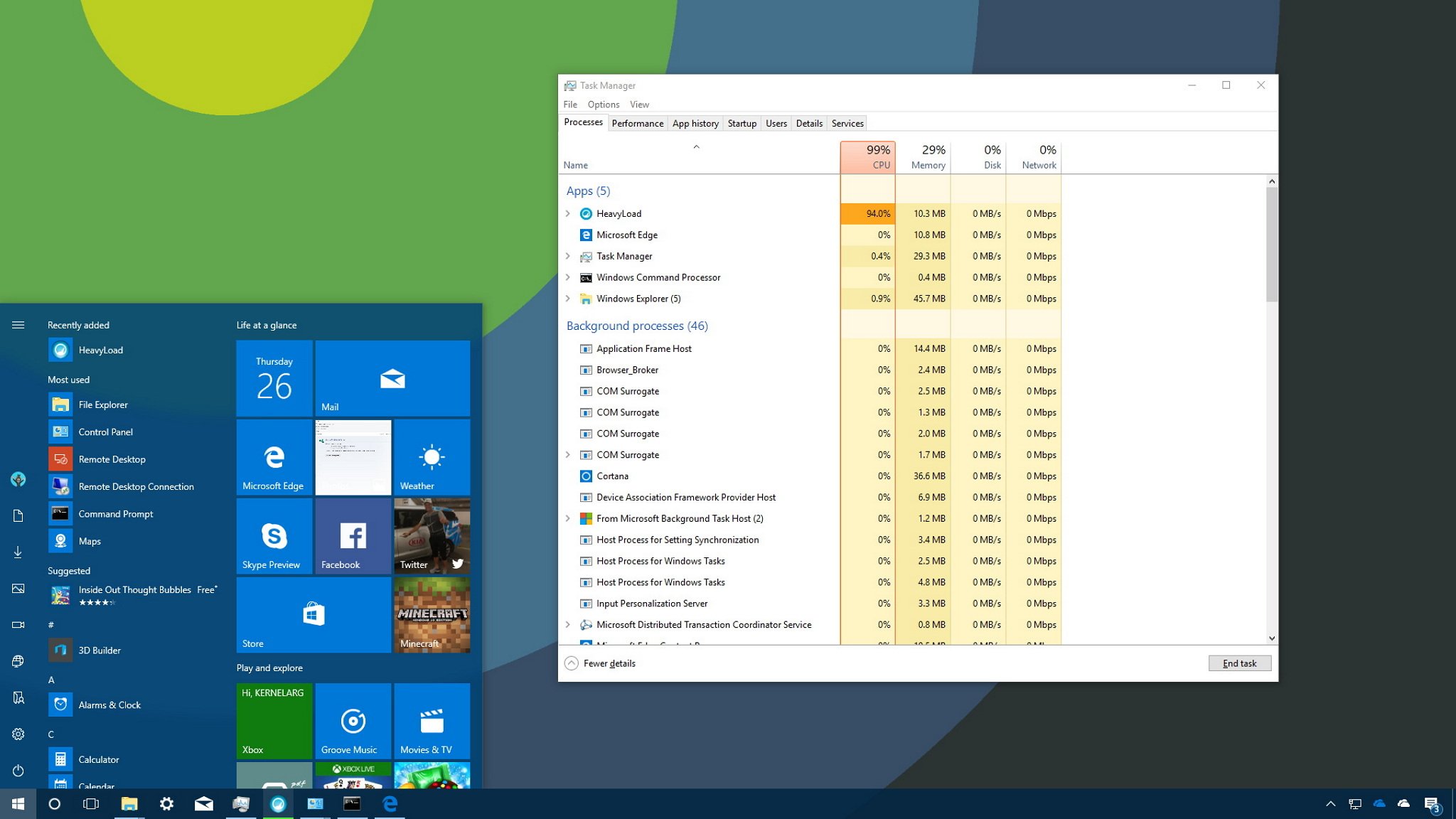
When you’re in advanced mode, you’ll see a number of tabs, including «Performance», «App history», «Startup», «Users», «Details», «Services», and the one we’re interested in, the «Processes» tab. Typically, the Processes tab is the first place you want to go to detemine which process is draining your computer’s resources. This tab lists all the running processes in a single view grouped by «Apps», «Background processes» and «Windows Processes». On Windows 10, you can also find multiple instances or other processes under the same process, which helps you to better understand how they’re organized and how they use system resources.
You can always expand a group to see all the processes by clicking the chevron-right icon or by right-clicking the item and selecting Expand. Usually, you’ll see groups for Windows processes when opening multiple tabs on your web browser or multiple File Explorer windows, for example.
Identifying processes with high-resource usage
If an application is not responding, a website is taking a long time to load, or your system fan starts getting loud, you can quickly use Task Manager to troubleshoot the problem. In the Processes tab, the first thing you want to look at is the percentage of the total resource use for the processor, memory, hard drive and network. You can click the column names to sort the list and bring to the top the ones using the most resources. If you see any of these resources running high (90 percent or higher), you might have found the problem.
Task Manager also uses colors to highlight processes that use the most resources. You’ll notice that as a process starts to consume more resources, the color begins to change from a light- to a dark-shade of orange, making it easier to tell which one is causing the problem.
Typically, when you’re not actively using applications and your computer isn’t working on anything specific, such as maintenance, your total CPU usage should be less than 30 percent. Applications that are running, even if you’re not using them, and processes use part of your computer’s memory, and that usage will increase as you use or launch more applications. Memory usually won’t be an issue unless you run out of it, in which case your computer will start using virtual memory, and that can cause your PC to slow down. Generally speaking, depending on your system configuration, your total memory usage should be below 60 percent. If you’re not copying files or rendering videos, disk usage should be below 5 percent.
Network connectivity is almost never the reason your system is slow, but there could be a problem in the network causing web content to take a long time to load. If you’re having problems downloading files, and you see «Network» stuck at 0 percent, you may have an idea of what’s going on.
Stopping processes with high-resource usage
After you identify the problem, right-click the process, and select End task to terminate it. Alternatively, you can simply select the item and click the End task button in the bottom-right corner.
While stopping a process using the Task Manager will most likely stabilize your computer, ending a process can completely close an application or crash your computer, and you could lose any unsaved data. It’s always recommended to save your data before killing a process, if possible.
If you’re not sure about how the process you’re trying to terminate affects your PC, you can right-click it, and select the Search online option. This action opens your web browser and displays a search result with more information about the process. Windows 10 is also smart enough to let you know if you’re about to end an essential system process that can crash your computer.
Wrapping things up
Although there are many other ways to troubleshoot system performance, Task Manager gives you an easy way to find out at a glance why your computer is slow or if an app is not responding, and then quickly act on it. You can end an application that isn’t responding using Task Manager in compact mode, but the advanced view gives you more information about processes that are acting up in Windows 10.
More Windows 10 resources
For more help articles, coverage, and answers to common Windows 10 questions, visit the following resources:
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
In this guide, we’ll show you the steps to get rid of the update KB5001330 to fix profile, gaming, and BSoD problems with the Windows 10 October 2020 Update and May 2020 Update.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!
tasklist tasklist
Отображает список запущенных в данный момент процессов на локальном или удаленном компьютере. Displays a list of currently running processes on the local computer or on a remote computer. Tasklist заменяет средство TList . Tasklist replaces the tlist tool.
Эта команда заменяет средство TList . This command replaces the tlist tool.
Синтаксис Syntax
Параметры Parameters
| Параметр Parameter | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| ключ /s | Указывает имя или IP-адрес удаленного компьютера (не используйте символы обратной косой черты). Specifies the name or IP address of a remote computer (do not use backslashes). По умолчанию это локальный компьютер. The default is the local computer. |
| /u \ /u \ | Выполняет команду с разрешениями учетной записи пользователя, заданного или пользователем \ . Runs the command with the account permissions of the user who is specified by or by \ . Параметр /u может быть указан только в том случае, если задано также значение /s . The /u parameter can be specified only if /s is also specified. По умолчанию заданы разрешения пользователя, который в данный момент вошел в систему компьютера, выполняющего команду. The default is the permissions of the user who is currently logged on to the computer that is issuing the command. |
| /p |
| Указывает формат, используемый для выходных данных. Specifies the format to use for the output. Допустимые значения: Table, List и CSV. Valid values are table, list, and csv. Формат выходных данных по умолчанию — Table. The default format for output is table. | |
| использован /nh | Подавляет вывод заголовков столбцов в выходных данных. Suppresses column headers in the output. Допустим, если для параметра /FO задано значение Table или CSV. Valid when the /fo parameter is set to table or csv. |
| /Fi /fi | Указывает типы процессов, включаемых в запрос или исключаемых из него. Specifies the types of processes to include in or exclude from the query. Можно использовать более одного фильтра или использовать подстановочный знак ( \ ) для указания всех задач или имен изображений. You can use more than one filter or use the wildcard character ( \ ) to specify all tasks or image names. Допустимые фильтры перечислены в разделе имена фильтров, операторы и значения этой статьи. The valid filters are listed in the Filter names, operators, and values section of this article. |
| /? /? | Отображение справки в командной строке. Displays help at the command prompt. |
Имена фильтров, операторы и значения Filter names, operators, and values
| Имя фильтра Filter Name | Допустимые операторы Valid Operators | Допустимые значения Valid Value(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Состояние STATUS | eq, ne eq, ne | RUNNING | NOT RESPONDING | UNKNOWN . RUNNING | NOT RESPONDING | UNKNOWN . Этот фильтр не поддерживается, если указана удаленная система. This filter isn’t supported if you specify a remote system. |
| IMAGENAME IMAGENAME | eq, ne eq, ne | Имя образа Image name |
| ИД процесса PID | eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le | Значение PID PID value |
| SESSION SESSION | eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le | Номер сеанса Session number |
| SESSIONNAME SESSIONNAME | eq, ne eq, ne | Имя сеанса Session name |
| CPUtime CPUtime | eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le | Время ЦП в формате чч: мм: СС, где mm и SS находятся в диапазоне от 0 до 59, а чч — любое число без знака CPU time in the format HH:MM:SS, where MM and SS are between 0 and 59 and HH is any unsigned number |
| мемусаже MEMUSAGE | eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le | Использование памяти в КБ Memory usage in KB |
| USERNAME USERNAME | eq, ne eq, ne | Любое допустимое имя пользователя ( или ) Any valid user name ( or ) |
| Обслуживание SERVICES | eq, ne eq, ne | Имя службы Service name |
| WINDOWTITLE WINDOWTITLE | eq, ne eq, ne | Заголовок окна. Window title. Этот фильтр не поддерживается, если указана удаленная система. This filter isn’t supported if you specify a remote system. |
| МОДУЛЕ MODULES | eq, ne eq, ne | Имя DLL DLL name |
Примеры Examples
Чтобы получить список всех задач с идентификатором процесса, превышающим 1000, и отобразить их в формате CSV, введите: To list all tasks with a process ID greater than 1000, and display them in csv format, type:
Чтобы получить список системных процессов, выполняемых в данный момент, введите: To list the system processes that are currently running, type:
Чтобы вывести подробные сведения обо всех выполняющихся процессах, введите: To list detailed information for all processes that are currently running, type:
Чтобы получить список всех сведений о службе для процессов на удаленном компьютере срвмаин с именем DLL, начинающимся с NTDLL, введите: To list all the service information for processes on the remote computer srvmain, which has a DLL name beginning with ntdll, type:
Чтобы получить список процессов на удаленном компьютере срвмаин, используя учетные данные текущей учетной записи пользователя, выполнившего вход в систему, введите: To list the processes on the remote computer srvmain, using the credentials of your currently logged-on user account, type:
Чтобы получить список процессов на удаленном компьютере срвмаин, используя учетные данные хироплн учетной записи пользователя, введите: To list the processes on the remote computer srvmain, using the credentials of the user account Hiropln, type: