- How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
- How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
- Opening Task Manager
- Understanding the Processes tab
- Identifying processes with high-resource usage
- Stopping processes with high-resource usage
- Wrapping things up
- More Windows 10 resources
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
- Task Manager Processes tab completely blank
- Replies (13)
- Windows task manager: Viewing Windows 7 processes and applications
- If applications or processes in a customer’s Windows 7 operating system aren’t responding, you can use the task manager to view, end and restart them.
- Microscope UK
- HPE and Konica Minolta emphasising sustainability
- Channel plugging the multicloud skills gap
- NEC, LogicMonitor and ImmuniWeb bolster channel numbers
- Search Security
- 6 SSH best practices to protect networks from attacks
- Companies must train their SOC teams well to prevent breaches
- Risk & Repeat: FBI’s web shell removal raises questions
- Search Storage
- Engineering firm thwarts ransomware attack with Nasuni
- 8 best practices for SAN deployment within SMBs
- A close look at NetApp Cloud Volumes Service for Google Cloud
- Search Networking
- Aruba product integrations advance its SASE strategy
- Wi-Fi 6 rollout requires careful review of network devices
- How cloud-native networking will transform infrastructure
- Search Cloud Computing
- Ready to be a GCP architect? Try this quiz and see
- Choose the right serverless container service
- IBM boosts vertical cloud push with financial services cloud
- Search Data Management
- Who belongs on a high-performance data governance team?
- Soda launches cloud service to improve data observability
- Bigeye raises $17M Series A funding to boost data quality
- Search Business Analytics
- Insightsoftware acquisition of Izenda targets embedded BI
- Data scientist shortage leaves organizations uncertain
- Air Force’s data overhaul makes analytics a priority
How to use Windows 10 Task Manager to kill processes that drain resources
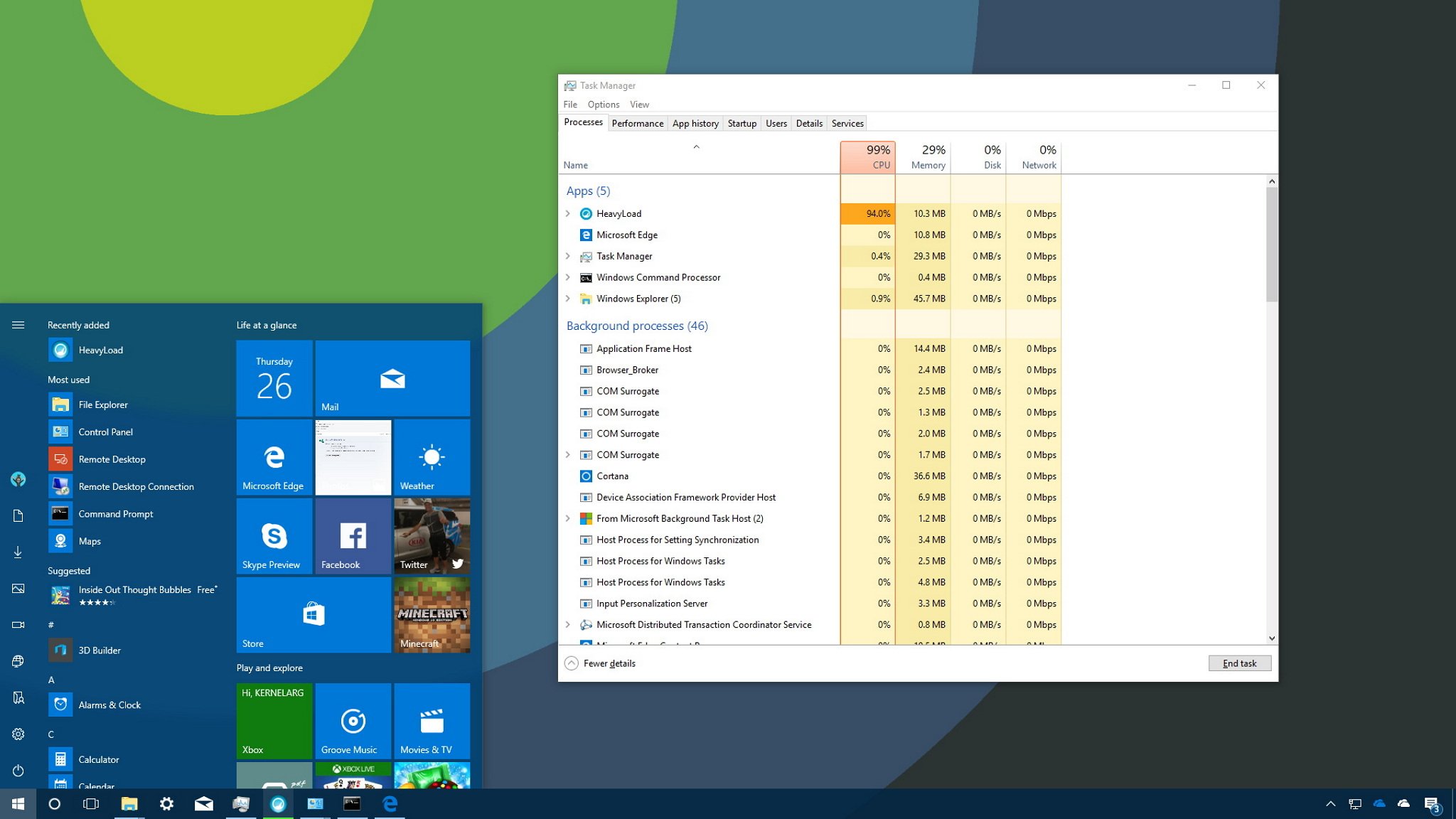
The Task Manager is an advanced tool that comes with Windows 10, and it provides a number of tabs that allow you to monitor the applications, processes and services running on your computer. However, you’ll likely find yourself using the Processes tab more than anything else, because it lets you quickly see how system resources are utilized, which can be very helpful when trying to troubleshoot applications or find out why your computer is suddenly slow.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to use Task Manager to identify and stop processes that use excessive system resources, to keep your computer at top speeds.
How to use Task Manager to manage high-resource processes
Opening Task Manager
If you want to use Task Manager to view and stop processes with high-resource usage, you first need to know how to open the tool. Here are a few ways to open Task Manager:
- Right-click the Taskbar and click on Task Manager.
- Open Start, do a search for Task Manager and click the result.
- Use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut.
- Use the Ctrl + Alt + Del keyboard shortcut and click on Task Manager.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the power-user menu and click on Task Manager.
If this is your first time opening Task Manager, the tool will probably open in compact mode, which only lists running applications. Click the More details button to access Task Manager in advanced mode.

Understanding the Processes tab
When you’re in advanced mode, you’ll see a number of tabs, including «Performance», «App history», «Startup», «Users», «Details», «Services», and the one we’re interested in, the «Processes» tab. Typically, the Processes tab is the first place you want to go to detemine which process is draining your computer’s resources. This tab lists all the running processes in a single view grouped by «Apps», «Background processes» and «Windows Processes». On Windows 10, you can also find multiple instances or other processes under the same process, which helps you to better understand how they’re organized and how they use system resources.
You can always expand a group to see all the processes by clicking the chevron-right icon or by right-clicking the item and selecting Expand. Usually, you’ll see groups for Windows processes when opening multiple tabs on your web browser or multiple File Explorer windows, for example.
Identifying processes with high-resource usage
If an application is not responding, a website is taking a long time to load, or your system fan starts getting loud, you can quickly use Task Manager to troubleshoot the problem. In the Processes tab, the first thing you want to look at is the percentage of the total resource use for the processor, memory, hard drive and network. You can click the column names to sort the list and bring to the top the ones using the most resources. If you see any of these resources running high (90 percent or higher), you might have found the problem.
Task Manager also uses colors to highlight processes that use the most resources. You’ll notice that as a process starts to consume more resources, the color begins to change from a light- to a dark-shade of orange, making it easier to tell which one is causing the problem.
Typically, when you’re not actively using applications and your computer isn’t working on anything specific, such as maintenance, your total CPU usage should be less than 30 percent. Applications that are running, even if you’re not using them, and processes use part of your computer’s memory, and that usage will increase as you use or launch more applications. Memory usually won’t be an issue unless you run out of it, in which case your computer will start using virtual memory, and that can cause your PC to slow down. Generally speaking, depending on your system configuration, your total memory usage should be below 60 percent. If you’re not copying files or rendering videos, disk usage should be below 5 percent.
Network connectivity is almost never the reason your system is slow, but there could be a problem in the network causing web content to take a long time to load. If you’re having problems downloading files, and you see «Network» stuck at 0 percent, you may have an idea of what’s going on.
Stopping processes with high-resource usage
After you identify the problem, right-click the process, and select End task to terminate it. Alternatively, you can simply select the item and click the End task button in the bottom-right corner.
While stopping a process using the Task Manager will most likely stabilize your computer, ending a process can completely close an application or crash your computer, and you could lose any unsaved data. It’s always recommended to save your data before killing a process, if possible.
If you’re not sure about how the process you’re trying to terminate affects your PC, you can right-click it, and select the Search online option. This action opens your web browser and displays a search result with more information about the process. Windows 10 is also smart enough to let you know if you’re about to end an essential system process that can crash your computer.
Wrapping things up
Although there are many other ways to troubleshoot system performance, Task Manager gives you an easy way to find out at a glance why your computer is slow or if an app is not responding, and then quickly act on it. You can end an application that isn’t responding using Task Manager in compact mode, but the advanced view gives you more information about processes that are acting up in Windows 10.
More Windows 10 resources
For more help articles, coverage, and answers to common Windows 10 questions, visit the following resources:
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
In this guide, we’ll show you the steps to get rid of the update KB5001330 to fix profile, gaming, and BSoD problems with the Windows 10 October 2020 Update and May 2020 Update.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!
Task Manager Processes tab completely blank
I’ve seen other posts of users having this issue.
In minimal view, the task manager shows nothing other than «There are no running apps».
When I click «More details», I get the full view, but the Processes tab shows no processes. All the other tabs are working as expected, the problem is only with the Processes tab.
If I reboot the PC, the task manager works fine at first. But later it becomes blank again.
Every thread has someone suggesting SFC and DISM to repair Windows image.
I tried all of them. No result.
This has been happening ever since Fall Creators update, on two different computers. One computer is brand new, was clean from factory.
Replies (13)
* Please try a lower page number.
* Please enter only numbers.
* Please try a lower page number.
* Please enter only numbers.
The blank Task Manager issue might be due to a software conflict. That being said, we’ll need additional information to properly address your concern. Kindly answer the following:
- Are you getting any error messages?
- Aside from running the DISM command-line tool and the SFC tool, what other troubleshooting steps have you tried so far?
- Have you installed the latest updates for Windows 10?
- What is the current OS Build of your Windows 10 device? Click the Start button, type About your PC , press Enter , and then scroll down to Windows specifications to find this information.
For now, we recommend performing a clean boot in order to determine if an installed program is causing the issue. A clean boot is performed to start Windows by using a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This helps eliminate software conflicts that occur when you use your Windows 10 PC. For the steps on how to perform this operation, kindly refer to this support article.
NOTE : Please go to the section: Reset the computer to start normally after clean boot troubleshooting to boot the PC in normal startup after fixing the issue.
Windows task manager: Viewing Windows 7 processes and applications
If applications or processes in a customer’s Windows 7 operating system aren’t responding, you can use the task manager to view, end and restart them.
Solutions provider takeaway: You can use the task manager to view Windows 7 applications and processes, and you can also end and restart them if they’re unresponsive. The task manager has six tabs in all, including the performance tab that displays usage graphs.
 | ||||
|  | |||
 | ||||
Task Manager, for many of us, is our «go-to» tool for solving problems. You have a problem, you go to Task Manager—it’s almost ingrained in us. You’ll see immediate information about your processes, CPU usage, memory, network, and so forth.
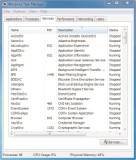
For one thing, the first time you start Task Manager, you’ll notice that you can now choose to see processes from all the users of the system. One thing you’ll notice right away is the Description aspect to the Processes tab and the Services tab (see Figure 11.8). This was added in Vista.
One of the new features of Task Manager is the ability to create a mini-dump file of an application that is running. You can right-click an application or process that is running and choose Create Dump File, which displays a dialog box that shows you where that file has been written. You can use this feature to discover why a particular application might be crashing so often. Or if a process has already crashed and is no longer responding, you can try to discover the cause.
Figure 11.8 Task Manager showing the descriptions and options for Services.
Task Manager has six tabs:
- Applications
- Processes
- Services
- Performance
- Networking
- Users
In addition to the tabs, there is a menu at the top that serves up even more options that we’ll also cover in the following section. Let’s start by looking at the Applications tab.
This is the starting point for Windows Task Manager and there is more here than meets the eye. The Task column displays a list of open applications. This is a live look at your system. If you close one of the applications, it removes itself from this list.
The Status column shows whether the application is Running or Not Responding. This simple layout allows you to quickly see what application is acting up. At the bottom are three buttons:
- End Task: Closes an application or process.
- Switch To: Switches between applications or processes.
- New Task: Starts an application from the dialog box that opens when you click this button.
Below these buttons are real-time information regarding Processes, CPU Usage, and the amount of used Physical Memory. At a glance, you can see what resource is affected by this view in the Task Manager.
Using Task Manager to End an Application
The following steps show you how to use Task Manager to end an application.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- In the Task area, locate an application that is running and click it.
- Click the End Task button.
With this simple process, you see how easy it is to close an application. Of course, the purpose of Task Manager is to help you troubleshoot and cope with crashed applications, not ones that are working fine. So the next time an application hangs too long, follow the above steps again. When an application hangs too long, the Status column shows Not Responding. Clicking End Task should close the application.
On rare occasion, an application might stubbornly stay open despite your attempts to end it. In this situation, press Ctrl+Alt+Del again and repeat the steps to close it.
Using Task Manager to Start an Application
The following steps show you how to use Task Manager to start an application. In this example, you learn to end explorer.exe and restart it through Task Manager.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- Click the Processes tab.
- In the Image Name column, locate explorer.exe.
- Click the End Process button. Windows Explorer closes but all other applications, including Task Manager, remain open.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Click the New Task button. The Create New Task dialog box opens.
- In the Open text box, type explorer.
- Click OK. Windows Explorer opens.
The Create New Task button comes in handy in situations that call for you to reopen an application. If you know the path to the application, you can enter it; otherwise, you can click the Browse button to navigate to the application name.
One other option to mention on the Applications tab appears when you right-click any application. You will find Create Dump File. Dump files capture data from the application that you can share with software developers and programmers who are trying to determine why an application crashes or has other faults. The dump file is saved locally and is a copy of what the application looks like in memory. You can send it to your help and support department, which can analyze its contents.
This tab gives you a bird’s-eye view of all your processes, including a button to Show Processes from all Users and the aforementioned End Process button. The Process tab is invaluable if your computer is running slow for an undetermined reason. By viewing the Image Name, CPU, Memory, and Description columns, you can focus on the precise area causing trouble.
Using Task Manager to Monitor an Application’s CPU and Memory Usage
The following steps show you how to monitor an application’s CPU and memory usage. In this example, you monitor Windows Media Player.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- Click the Processes tab.
- While still keeping the Task Manager in view on-screen, open Windows Media Player. As the application opens, watch the CPU and Memory columns for the information it displays for Windows Media Player. (You may need to resize the column to see the heading names.)
- Close Windows Media Player.
- Open other applications and monitor their resource usage through the processes tab.
By viewing your process resource usage, it becomes evident very quickly which process is causing the problem. If you are looking for a specific process and you have several open, click Image Name to sort the column.
If a process is causing problem, it can be stopped by using the Processes tab—as you learn in the following section.
Using Task Manager to End a Process
This short exercise teaches you how to end a process through Task Manager. Use caution when doing this on applications not discussed in this exercise. Not ending a process safely can result in data loss or in rare cases, system instability.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- Click the Processes tab.
- Look at the Description column and select a process that you know (for example, select Windows Task Manager).
- Click the End Process button. You are asked to confirm this.
- Click End Process again. The process ends.
 | ||||
|  | |||
 | ||||
A quick way to find a process associated with an application is to first locate the app on the Applications tab, right-click it, and then choose Go To Process. This takes you to the Processes tab with the associated process highlighted.
If more than one user is logged-on to your machine when you run Task Manager and you are unable to see the process you are looking for, the Processes tab includes a Show Processes From All Users button that you can click to see any processes in use by other users logged on.
You can also right-click an application and choose Properties to access the properties of that particular executable. For example, you can change compatibility options, permissions, as well as other aspects of the program.
This tab shows you your services, some descriptive information regarding them (Description and Group information), and if they are running or not. You can use this tab to stop or start services.
Using Task Manager to Stop and Restart a Service
The following steps show you how to stop and restart a service through Task Manager.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- Click the Services tab.
- In the Description column, scroll down to Print Spooler, right-click it, and choose Stop Service.
- Depending on your security configuration, you might receive an access-denied message. If this is the case, click Print Spooler again.
- Click the Services button in the lower right.
- If a UAC window opens, click Yes.
- In the main pane, scroll down to Print Spooler, right-click it, and choose Stop.
- To restart the service, follow these same steps, but when you right-click Print Spooler, and choose Start instead.
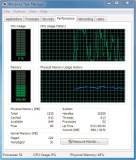
This tab includes a feature that is new to Windows 7 (although you might not notice it). Under Physical Memory (MB) group, Vista features Total, Cached, and Free. Windows 7 has added Available to that group.
- Total: The amount of RAM installed on the system in MB.
- Cached: The amount of physical RAM used for system resources.
- Available: The total of standby and free memory for programs.
- Free: The amount of memory that is currently unused or doesn’t contain useful information.
The Performance tab also includes the Resource Monitor button. This is a logical location since you might be coming to the Performance tab to troubleshoot a problem. You can usually find what you are looking for in the CPU and Memory Usage graphs (see Figure 11.9). If you can’t find it there, click the Resource Monitor button to access a plethora of monitoring tools.
Figure 11.9 Get real-time stats in the Performance tab.
The Networking tab shows a graph of your active network connection, where you can view the network utilization of your connections. The bottom of this tab also includes columns showing the Link Speed and the connection State.
This tab shows you the users who are logged on now. By right-clicking a user, you can Disconnect a user who is remotely connected to your computer or Log Off a local user.
Using Task Manager to Log-Off a Local User
The following steps show you how to log-off a local user through Task Manager. To complete this exercise, you will need multiple users logged-on at once.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- Click Start Task Manager.
- Click the Users tab.
- Right-click the User you would like to log off and choose Log Off.
- A warning message appears, asking you to confirm that you want to log off this user (because the user’s unsaved data might be lost). Click Log Off User and the user is logged off.
There are a few notable selections available on the Task Manager menu:
- On the File menu, you can select New Task to open a program (just as you can by using the Applications tab).
- On the View menu, you can adjust the refresh speed of the monitoring of your incoming resources. To see faster refreshes on your incoming data for CPU and Memory, go to View, click Update Speed, and then choose High.


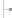
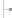
Printed with permission from Que Publishing. Copyright 2010. Using Microsoft Windows 7 by J. Peter Bruzzese. For more information about this title and other similar books, please visit http://www.quepublishing.com.
Using Task Manager to monitor memory usage in Windows 10
How to reduce the number of clicks in Salesforce
What are my options for configuring Windows 8 startup?
Managing desktop processes with Mac Activity Monitor
- Microapps Empower the Modern Workforce –Citrix
- Making an Intelligent Workspace a Part of Your Everyday Reality –Citrix
- Transform Your IT Organization with Automation and Converged and Hyperconverged. –Dell Technologies
- See More
- How to reduce the number of clicks in Salesforce – SearchCustomerExperience
- Optimizing Windows 7 application performance – SearchITChannel
- Microsoft Windows 7 Task Manager troubleshooting tips – SearchEnterpriseDesktop
Microscope UK
HPE and Konica Minolta emphasising sustainability
Firms get backing of independent organisations looking to promote green practices and corporate social responsibility
Channel plugging the multicloud skills gap
VMware virtual cloud event highlights the vital role that partners are playing in helping customers navigate a cloud world
NEC, LogicMonitor and ImmuniWeb bolster channel numbers
Firms reveal progress made so far this year in bringing fresh partners on board as they widen their channel bases
Search Security
6 SSH best practices to protect networks from attacks
SSH is essential, but default installations can be costly. Auditing and key management are among critical SSH best practices to .
Companies must train their SOC teams well to prevent breaches
SOC teams can have all the latest and greatest cybersecurity tools, but unless they have the proper training, it won’t be enough .
Risk & Repeat: FBI’s web shell removal raises questions
The FBI accessed computers — without the knowledge or consent of the owners — to remove hundreds of web shells placed in .
Search Storage
Engineering firm thwarts ransomware attack with Nasuni
Ransomware got in through an exploit in an older version of SQL Server, but Dennis Group used Nasuni to restore its systems back .
8 best practices for SAN deployment within SMBs
SMBs face a number of challenges when planning and performing a SAN implementation. Get out in front of an often intricate .
A close look at NetApp Cloud Volumes Service for Google Cloud
Compared to other versions of the NetApp Cloud Volumes Service, the software-defined edition on Google Cloud has some key .
Search Networking
Aruba product integrations advance its SASE strategy
Aruba’s latest SASE-related integrations involve the Silver Peak-based SD-WAN, Threat Defense and the ClearPass Policy Manager. .
Wi-Fi 6 rollout requires careful review of network devices
Wi-Fi 6 is just one part of the overall enterprise network. Organizations need to evaluate several network components to ensure a.
How cloud-native networking will transform infrastructure
Cloud-native networking aims to prioritize business needs and enable networks to become more efficient. Learn more about the .
Search Cloud Computing
Ready to be a GCP architect? Try this quiz and see
This 10-question quiz, drawn from a new GCP certified professional cloud architect prep guide, helps identify your strengths and .
Choose the right serverless container service
Many IT pros consider serverless containers to be largely hype, while others say it offers real advances in serverless computing.
IBM boosts vertical cloud push with financial services cloud
IBM doubles down on its investment in vertical markets, rolling out a financial services cloud that shares workloads with clouds .
Search Data Management
Who belongs on a high-performance data governance team?
Putting together a high-quality data governance team can be a challenge. Explore the necessary team members and best practices .
Soda launches cloud service to improve data observability
Data quality vendor Soda has had a busy 2021, building out new services and raising funding to help organizations identify and .
Bigeye raises $17M Series A funding to boost data quality
The former Uber product manager and current CEO and co-founder of a startup outlines the challenges and opportunities of enabling.
Search Business Analytics
Insightsoftware acquisition of Izenda targets embedded BI
ERP vendor Insightsoftware acquired embedded analytics specialist Izenda on April 15, marking its second purchase of an embedded .
Data scientist shortage leaves organizations uncertain
Despite their desire to use data science in their decision-making process, some organizations can’t find qualified data .
Air Force’s data overhaul makes analytics a priority
With its data locked in legacy systems that didn’t communicate with one another, in 2017 the Air Force started to overhaul of its.