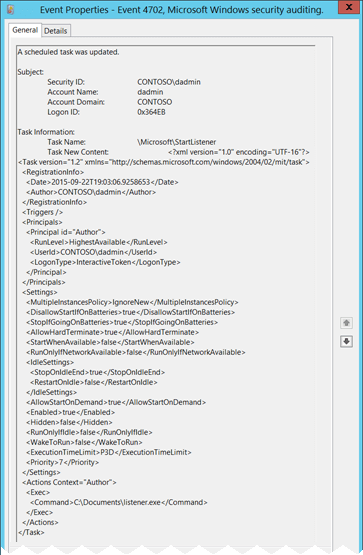
- 4702(S): A scheduled task was updated.
- Security Monitoring Recommendations
- Windows 10: Компьютер сам просыпается рано утром
- Description of the scheduled tasks in Windows Vista
- INTRODUCTION
- More Information
- Scheduled tasks
- Hidden scheduled tasks
- Additional information
- The Mcupdate scheduled task
- The scheduled tasks in the SideShow folder
- The CrawlStartPages scheduled task
- The UPnPHostConfig scheduled task
- References
4702(S): A scheduled task was updated.
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
Event Description:
This event generates every time scheduled task was updated/changed.
NoteВ В For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
Windows 10 Versions 1903 and above augments the event with these additional properties: Event Version 1. Event XML:
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that requested the “change/update scheduled task” operation. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
NoteВ В A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that requested the “change/update scheduled task” operation.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is “NT AUTHORITY”.
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: “Win81”.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Task Information:
- Task Name [Type = UnicodeString]: updated/changed scheduled task name. The format of this value is “\task_path\task_name”, where task_path is a path in Microsoft Task Scheduler tree starting from “Task Scheduler Library” node:
- Task New Content [Type = UnicodeString]: the new XML for the updated task. Here “XML Task Definition Format” you can read more about the XML format for scheduled tasks.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4702(S): A scheduled task was updated.
Monitor for updated scheduled tasks located in the Task Scheduler Library root node, that is, where Task Name looks like вЂ\TASK_NAME’. Scheduled tasks that are created manually or by malware are often located in the Task Scheduler Library root node.
In the updated scheduled task, if the Task Content: XML contains Password value, trigger an alert. In this case, the password for the account that will be used to run the scheduled task will be saved in Credential Manager in cleartext format, and can be extracted using Administrative privileges.
Windows 10: Компьютер сам просыпается рано утром
Сегодня мне приснился сон: я рассказывал жене, что узнаю играющий трек и вот-вот пойдет «расколбас». Трек был от одного из моих любимых продюсеров Евгения Смирнова. Спустя пару секунд, я проснулся и действительно довольно громко в соседней комнате играл трек от Omnia и всё бы ничего, если бы на часах не было время 4:45 утра. Продрав глаза, я подумал, что кошка шарилась по моему столу и нажав кнопку на клавиатуре, вывела комп из режима «Сон». Однако, когда я встал с кровати, увидел кошку мирно спящую «в ногах». Я выключил комп и пошел спать дальше. Что же произошло? Какого хрена комп сам включился?
Оказывается, все довольно просто. На этот раз, это был не Google Chrome, а Windows 10, решивший что именно сейчас ему надо обновить Orchestrator. Что это за такая важная приблуда, я не особо разобрался.. да и не важно.
Самое главное, что я хотел бы рассказать, это как найти и обезвредить подобное поведение, ведь все мы любим ночью спать.
Все примеры (скриншоты) привожу для Windows 10, для более ранних версий этапы должны быть очень похожими или точно такими же..
- Самое первое, что нужно сделать в случае если у Вас такое произошло, это разобраться кто именно и каким образом вернул компьютер из режима «Сон». Для этого, нажимаем правой кнопкой на «Пуск» (в Windows 10) или на «Мой компьютер» (в предыдущих версиях) и выбираем пункт «Управление компьютером»:
Так же существует еще один способ запуска, данной оснастки: нажать Win+R и в открывшееся окно ввести compmgmt.msc
В открывшемся окне, в левой его части, в дереве выбрать такой путь:
— Управление компьютером
— Служебные программы
—— Просмотр событий
———- Журналы Windows
————— Система
Системный журнал событий Windows
4:45. В принципе, если вы выключили компьютер, например в 19:00, а включился он только в
4-5, то вы без проблем найдете этот разрыв:
Виновник выхода ПК из сна
Система вышла из состояния пониженного энергопотребления.
Время перехода в спящий режим: 2015-08-19T16:32:28.789995400Z
Время выхода из спящего режима: 2015-08-20T01:44:32.479224100Z
Источник выхода: Таймер — Будет выполнено назначенное задание «NT TASK\Microsoft\Windows\UpdateOrchestrator\Reboot», запросившее вывод компьютера из спящего режима.
Тут мы видим, во-первых, что произошло, а во вторых, кто вывел систему из сна. В нашем случае это «NT TASK\Microsoft\Windows\UpdateOrchestrator\Reboot«, запоминаем этот путь.
Теперь когда мы знаем виновника, настала пора его наказать. Для этого открываем планировщик заданий. Сделать это можно либо в этом же окне, либо нажав Win+R и написав туда: taskschd.msc . Я буду делать все в том же окне:
Отключение пробуждения ПК
Теперь вы знаете, как найти и обезвредить задания, которые пробуждают ваш ПК среди ночи..
Честно говоря, я не знаю чем думали разработчики, установив подобную задачу, но знаю точно, головой думали мало..
Желаю всем спокойных снов 🙂
— [добавлено 30.08.2015] —
Проснувшись сегодня утром, я опять обнаружил свой ПК включенным. Изучив события, я опять наткнулся на Orchestrator. Как оказалось, это событие, создается другим приложением, и его отключение не повлияет на его повторный запуск (т.к. оно будет пересоздано). Немного погуглив, я наткнулся на топик: Computer wakes up every night from sleep, здесь предложили такое решение:
I came to this thread after updating to Windows 10 and encountering issues with my computer not staying asleep when I came back to it the next day. I had not thought of looking in the group policy details for this kind of a setting. Here I thought I was being pretty savvy just going to the Event Viewer to find the root of my problem 🙂
I found your advice useful, but I think there might be a more broad solution for anyone who «just wants their computer to stay asleep.» I say this because this is not the first thing in the event logger that I’ve found as a cause of my computer waking. (Media Center updates with this scheduled task ‘NT TASK\Microsoft\Windows\Media Center\mcupdate_scheduled’ were also causing the computer to wake).
As I read through the documentation in the group policy editor for the ‘Enabling Windows Update Power Management to automatically wake up the system to install scheduled updates’ setting, it says «Specifies whether the Windows Update will use the Windows Power Management features to automatically wake up the system from hibernation, if there are updates scheduled for installation.»
This made me wonder. what are my settings in power management that relate to allowing it to wake? I then found that in Control Panel > Power Options > Edit Plan Settings > Change advanced power settings you can then expand Sleep > Allow wake timers. Here you can choose
Your solution is certainly correct and concise, but if you want the nuclear option, this power management option seems to be a good solution.
Нас интересует выделенная часть. Вкратце в ней говорится, что в Плане управления питанием, есть опция позволяющая Разрешить/Запретить таймеры пробуждения. И что на самом деле, пробуждение компьютера занимается Windows Update который помимо всего прочего еще и перезагружает компьютер без вашего ведома.. Ну, что же попробуем это решение:
- Открываем настройки Электропитания, для этого нажимаем Win+R и в открывшееся окно вводим powercfg.cpl . Второй способ это:
Пуск>Параметры>Система>Питание и спящий режим>Доп. параметры питания - В открывшемся окне, нажимаем Настройка схемы электропитания
- Теперь нажимаем Изменить доп. параметры питания
- В открывшемся окне, раскрываем пункт Сон>Разрешить таймеры пробуждения и в пункте «Значения«, выбираем «Отключить
Отключение таймеров пробуждения
Надеюсь, теперь комп не будет просыпаться. И приход скайнета отложится до следующей переустановки винды 🙂
Description of the scheduled tasks in Windows Vista
INTRODUCTION
This article describes the scheduled tasks in a default installation of Windows Vista.
Note We do not recommend that you modify or disable a scheduled task in Windows Vista. Modifying or disabling a scheduled task may cause unexpected problems.
More Information
To view the scheduled tasks in a default installation of Windows Vista, click Start
Scheduled tasks
The following table describes the scheduled tasks in a default installation of Windows Vista.
This scheduled task runs the Bthudtask.exe program at an elevated permissions level. The Bthudtask.exe program removes a pairing with a remote Bluetooth device that has the specified service ID. The scheduled task exits after the device is uninstalled.
This scheduled task automatically wakes the computer and then puts the computer to sleep when the automatic waking feature is enabled for a Windows SideShow-compatible device.
This scheduled task manages and synchronizes metadata for the gadgets that are installed on a Windows SideShow-compatible device.
This scheduled task manages the session behavior when multiple user accounts exist on a Windows SideShow-compatible device.
This scheduled task runs when you log on to a user account. It provides system data for the clock, for the power source, for the wireless network strength, and for the volume on a Windows SideShow-compatible device.
This scheduled task runs when you start the computer. This scheduled task also runs as a daily task. This scheduled task runs the %windir%\system32\rundll32.exe srrstr.dll,ExecuteScheduledSPPCreation command to create regular system restore points.
This scheduled task runs when users log on. It provides operating system-initiated sounds such as navigation sounds.
This scheduled task indexes all the crawl-type start pages when the computer is idle.
This scheduled task runs the Gatherwirelessinfo.vbs file to collect wireless networking data. This scheduled task collects configuration information and state information about the computer. This information is displayed in a report. This information is included in the system logs. This information also appears in Performance Monitor.
This scheduled task runs the Gatherwiredinfo.vbs file to collect wired networking data. This scheduled task collects configuration information and state information about the system. This information appears in a report. This information also appears in the system logs. This information also appears in Performance Monitor.
This scheduled task runs the sc.exe config upnphost start= auto command to configure the UPnPHost service to start automatically.
This scheduled task runs the Lpremove.exe program when you start the computer. This scheduled task also runs one time when you install Windows Vista if a language pack that cannot be used is included. For example, this task removes language packs that are not needed when you install Windows Vista Home Basic. The Lpremove.exe program is in the System32 folder.
This scheduled task runs when you start the computer and after you modify the scheduled task. This scheduled task helps manage digital identities such as certificates, keys, and credentials for users and for the computer. This scheduled task also enables enrollment, roaming, and other services.
This scheduled task runs when you log on to a user account and after you modify the scheduled task. This scheduled task helps manage digital identities such as certificates, keys, and credentials for users and for the computer. This scheduled task also enables enrollment, roaming, and other services.
This scheduled task runs when a user connects or disconnects. This scheduled task also runs when a user locks or unlocks the computer to manage digital identities. This scheduled task manages certificates, keys, and credentials for users and for the computer. This scheduled task enables enrollment, roaming, and other services.
Customer Experience Improvement Program
This scheduled task runs the Wsqmcons.exe program when you install Windows Vista. This scheduled task also runs the Wsqmcons.exe program daily if the user consented to participate in the Windows Customer Experience Improvement Program. This program collects and sends usage data to Microsoft. The Wsqmcons.exe program is located in the System32 folder.
Customer Experience Improvement Program
This scheduled task runs the \System32\wsqmcons.exe -n 0x1C577FA2B69CAD0 command when you log on to a user account. This scheduled task prompts the Microsoft Windows Software Quality Metrics opt-in notification.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\system32\defrag.exe -c command to defragment hard disk drives.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\system32\defrag.exe -c -i command weekly to defragment hard disk drives.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\ehome\ehPrivJob.exe /DRMInit command. This command makes sure that Windows Media Digital Rights Management (WMDRM) is initialized correctly every time that the Media Center Receiver Service (EhRecvr.exe) is started.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\ehome\mcupdate command to check for Windows Media Center updates.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\ehome\ehPrivJob.exe /OCURActivate command. This command enables the OpenCable Unidirectional Cable Receivers (OCUR) product key.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\ehome\ehPrivJob.exe /OCURDiscovery command. This command line starts the EhPrivjob.exe program. The EhPrivjob.exe program looks for digital cable tuners that might be attached to the computer. If the program finds a new digital cable tuner, it registers the tuner and makes sure that the Digital Cable Receiver Device exception is configured in the Windows Firewall.
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\ehome\ehPrivJob.exe /DoUpdateRecordPath command to set Windows Media Center Recorder permissions.
This scheduled task runs when you log on to a user account. This scheduled task starts programs that are configured for Windows HotStart.
This scheduled task starts the Microsoft Transient Multi-Monitor Manager when a user logs on to a Windows user account.
This scheduled task runs when you log on to a user account. The NAPStatus UI scheduled task starts the Network Access Protection Home Page. This scheduled task may also run when an event 18 message is detected.
This scheduled task runs the rundll32 ndfapi.dll,NdfRunDllDuplicateIPOffendingSystem command when an event 4198 message is detected. This scheduled task informs the user of an IP address conflict.
This scheduled task runs the runddl32 ndfapi.dll,NdfRunDllDuplicateIPDefendingSystem command when an event 4199 message is detected. This scheduled task informs the user of an IP address conflict.
Windows Error Reporting
This scheduled task runs the %windir%\system32\wermgr.exe –queuereporting command when you log on to a user account. This scheduled task also runs every 30 hours to process Windows Error Reporting data.
Hidden scheduled tasks
To view the hidden scheduled tasks in a default installation of Windows Vista, follow these steps:
Click Start
On the View menu, click Show Hidden Tasks.
The following table describes the hidden scheduled tasks in a default installation of Windows Vista.
MP Scheduled Scan
This scheduled task runs the Windows Defender Mpcmdrun.exe scan -restrict command.
This scheduled task is started by the Diagnostic Policy Service in the appropriate user session.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure Resolution host enables interactive resolutions for system problems that are detected by the Diagnostic Policy Service. This scheduled task starts the Windows Disk Diagnostic User Resolver Wizard (Dfdwiz.exe) when a problem with a hard disk is detected.
This scheduled task runs when you start the computer. This scheduled task also runs every hour after you start the computer.
This task is a Microsoft Reliability Analysis task that processes system reliability data.
This scheduled task runs when an event ID 1502 is written to the System log.
This scheduled task reviews Group Policy for changes that are related to Remote Assistance. This scheduled task runs the Raserver.exe /offerraupdate command.
This scheduled task runs when you log on to a user account.
This scheduled task monitors the TextServicesFramework system service.
Additional information
The Mcupdate scheduled task
The Mcupdate scheduled task downloads the following data packages. These data packages are used by Windows Media Center in Windows Vista.
Directory Service: The Directory Service package lists the packages that are available in a region. The Directory Service package also provides information about how to obtain packages, about how frequently to download packages, and about when to download packages.
Client Update: The Client Update package contains updated regional information.
Sports (United States & Canada Only): The Sports package contains information about sporting events. This information is integrated with other Electronic Program Guide (EPG) information. .
Net TV (United States only): The Net TV package contains information about videos that are available on demand.
MCESpotlight: This package contains information about Online Spotlight applications that are available.
The scheduled tasks in the SideShow folder
When a user logs on to a user account, the scheduled tasks in the SideShow folder determine whether a Windows SideShow-enabled device is connected to the computer. If a Windows SideShow-enabled device is not connected to the computer, the scheduled task immediately exits. If a Windows SideShow-enabled device is connected to the computer, these tasks perform the specified functions to make sure that the Windows SideShow-enabled device works correctly.
The CrawlStartPages scheduled task
The CrawlStartPages task is part of Windows Search. The CrawlStartPages task determines whether any locations that are not notification based must be indexed. For example, the CrawlStartPages task runs if you add a universal serial bus (USB) flash drive to the index by using the Indexing Options item in Control Panel. The task runs when you add the USB flash drive if the USB flash drive uses the FAT file system, a FAT partition, or a CD-ROM location. If you have not added a location in the Indexing Options item, this task will start and then be completed immediately.
Note On hard disk drives that use the NTFS file system, Windows Search uses Update Sequence Number (USN) journaling and notification to determine when files are added, deleted, or edited. However, on hard disk drives that use the FAT file system or on other locations that are not notification based, the file timestamps must be verified against the index to determine whether the file must be indexed again.
The UPnPHostConfig scheduled task
The UPnPHostConfig task changes the startup type for the UPnP Host service. This task changes the startup type for the UPnP Host service from «manual» to «automatic» when the service is needed.
References
For more information about the RACAgent scheduled task, visit the following Microsoft TechNet Web site:
http://technet2.microsoft.com/WindowsVista/en/library/cd27c62d-4d63-41da-9695-c7c5287da49c1033.mspxFor more information about the TextServicesFramework system service, visit the following Microsoft MSDN Web site:
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa966199.aspxFor more information about the Diagnostic Policy Service, visit the following Microsoft TechNet Web site:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windowsvista/aa905076.aspxFor more information about the Bluetooth protocol task, visit the following Microsoft MSDN Web site:
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa362761.aspxFor more information about Windows SideShow, visit the following Microsoft MSDN Web site:
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms744147.aspxFor more information about how to use the System Restore tool, click the article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
936212 How to repair the operating system and how to restore the operating system configuration to an earlier point in time in Windows Vista
For more information about the UPnP architectural framework, visit the following Microsoft MSDN Web site: