- Вики IT-KB
- Инструменты пользователя
- Инструменты сайта
- Боковая панель
- Подключение к Wi-Fi с RADIUS аутентификацией WPA2 Enterprise в Login Window на macOS High Sierra
- Почему мой Mac запрашивает пароль WPA2?
- Как мне найти свой пароль WPA2 на Mac?
- Как мне узнать свой пароль WPA2?
- Пароль WPA2 совпадает с паролем WiFi?
- Как подключить мой Mac к WPA2 WiFi?
- Какова длина пароля WPA2?
- Как мне изменить свой пароль WPA2?
- Как мне найти свой пароль WPA2 на моем Iphone?
- Могу ли я увидеть пароль Wi-Fi, к которому я подключен?
- Что такое небо паролей WPA2?
- Где я могу найти пароль для своего роутера?
- Как мне настроить WPA2?
- Почему мой Mac не принимает мой пароль Wi-Fi?
- Почему мой Mac продолжает запрашивать пароль WIFI?
- В чем разница между WPA2 Personal и WPA2 Enterprise?
- Connecting Apple devices to 802.1X networks
- 802.1X configurations for Mac
- Trusting the Certificate Authority
- Requesting the AD Certificate
- Troubleshooting
Вики IT-KB
Пошаговые руководства, шпаргалки, полезные ссылки.
Инструменты пользователя
Инструменты сайта
Боковая панель
Подключение к Wi-Fi с RADIUS аутентификацией WPA2 Enterprise в Login Window на macOS High Sierra

Для того, чтобы разрешить системе подключаться к Wi-Fi на экране входа Login Window, нужно создать профиль. Но не всё так просто, как может казаться на первый взгляд.
Apple Configurator 2 не имеет опции Use as a Login Window configuration:
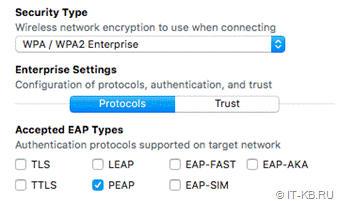
То, что нам нужно, есть только в Profile manager, который идёт в составе MacOS Server:
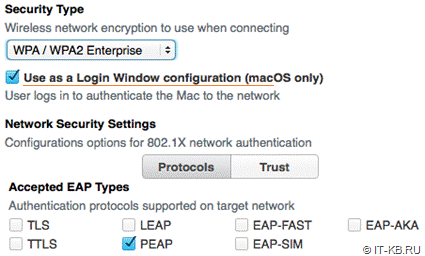
Профиль имеет XML-структуру. Мы можем сравнить файлы профилей с помощью FileMerge.app, входящего в пакет Xcode.app и сразу увидим необходимый нам параметр:
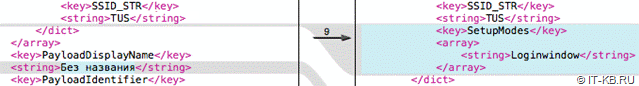
MacOS Server есть не у всех, а иметь возможность настраивать Wi-Fi на экране входа может понадобится любому администратору. Поэтому сначала создаём профиль Wi-Fi в Apple Configurator 2, а после открываем его на редактирование в текстовом редакторе.
После строки c SSID беспроводной сети добавляем фрагмент:
Сохраняем файл и двойным кликом добавляем профиль. Обращаем внимание на то, что появился пункт Корпоративный режим
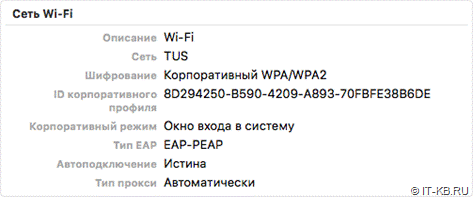
При установке профиля система не задаст дополнительных вопросов, так как подразумевается использование учётных данных, введённых на экране входа.
Отключаем компьютер от проводной сети и перезагружаемся.
После загрузки над полем ввода учётных данных появляется ниспадающий список:
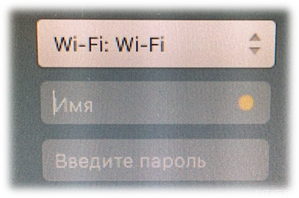
Вводим доменные учётные данные пользователя и видим, как сначала устанавливается соединение, а затем совершается вход в систему.
Проверено на следующих конфигурациях:
| Версия клиентской ОС |
|---|
| Apple macOS High Sierra (10.13.4) |

Виталий Якоб
Время публикации: 25.07.2018 16:13
Источник
Почему мой Mac запрашивает пароль WPA2?
«Для сети Wi-Fi требуется пароль WPA2» означает, что вам нужен правильный пароль для подключения к сети Wi-Fi на Mac. … Откройте Системные настройки / Сеть / WIFI / Дополнительно / TCP / IP и нажмите Продлить аренду DHCP. Я надеюсь, что это поможет некоторым с этой досадной проблемой.
Как мне найти свой пароль WPA2 на Mac?
- Откройте приложение Keychain Access и введите имя сети в поле «Найти».
- Имя сети должно появиться в списке.
- Дважды щелкните имя сети. …
- Щелкните Показать пароль. …
- После ввода имени пользователя и пароля администратора пароль WPA2 будет отображаться в поле «Показать пароль».
Как мне узнать свой пароль WPA2?
Самый распространенный способ найти настройки безопасности вашего Wi-Fi роутера, включая пароль WPA2, — это войти на страницу настроек вашего роутера в веб-браузере. Если производитель маршрутизатора предлагает мобильное приложение, вы также можете увидеть там настройки WPA2.
Пароль WPA2 совпадает с паролем WiFi?
Вы также увидите WPA2 — это та же идея, но более новый стандарт. Ключ WPA или ключ безопасности: это пароль для подключения к беспроводной сети. Его также называют ключом безопасности Wi-Fi, ключом WEP или парольной фразой WPA / WPA2. Это другое имя для пароля на вашем модеме или маршрутизаторе.
Как подключить мой Mac к WPA2 WiFi?
Чтобы установить защиту WPA2, откройте AirPort-Утилиту, выберите базовую станцию и нажмите «Настройка вручную». Щелкните значок AirPort на панели инструментов, затем перейдите на вкладку «Беспроводная связь», затем выберите «WPA2 Personal» в меню «Безопасность беспроводной сети».
Какова длина пароля WPA2?
Пароль для WPA и WPA2 может содержать от 8 до 63 символов. Чем длиннее, тем лучше, и следует избегать слов в словаре. Как долго — вопрос мнения. Многие предлагают пароль не менее 20 символов.
Как мне изменить свой пароль WPA2?
Изменить пароль WPA2
Щелкните Параметры беспроводной связи (расположены вверху). Щелкните Дополнительные параметры безопасности (слева). В разделе «Уровень 1» щелкните WPA2. Введите общий ключ (пароль), затем нажмите «Применить».
Как мне найти свой пароль WPA2 на моем Iphone?
Если вы хотите найти пароль беспроводной сети, вам нужно найти в KeyChain Access имя беспроводной сети, а затем дважды щелкнуть по этому элементу.
Могу ли я увидеть пароль Wi-Fi, к которому я подключен?
В разделе «Состояние Wi-Fi» выберите «Свойства беспроводной сети». В свойствах беспроводной сети выберите вкладку «Безопасность», затем установите флажок «Показать символы». Пароль вашей сети Wi-Fi отображается в поле Ключ безопасности сети.
Что такое небо паролей WPA2?
Имя пользователя по умолчанию — «admin», а пароль по умолчанию — «sky», или это ваш пароль по умолчанию, напечатанный на маршрутизаторе WiFi. Когда вы его подписали, прокрутите вниз, и вы увидите «Шифрование безопасности WPA2-PSK». Здесь вы можете установить пароль.
Где я могу найти пароль для своего роутера?
См. Пароль Wi-Fi на Android
(Если вы в настоящее время не подключены, вам нужно нажать «Сохраненные сети», чтобы увидеть другие сети, к которым вы подключались в прошлом.) Затем нажмите кнопку «Поделиться», и пароль сети появится под QR-кодом.
Как мне настроить WPA2?
Настройка WPA2-Enterprise для ОС Android
- Найдите сертификат в диспетчере сертификатов.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и экспортируйте.
- Откроется мастер экспорта сертификатов. Экспорт закрытого ключа. Выберите параметр, чтобы включить все пути сертификатов. Введите пароль и создайте имя файла.
Почему мой Mac не принимает мой пароль Wi-Fi?
Убедитесь, что ваш роутер прохладный, проверьте его местоположение и убедитесь, что ничто не блокирует сигнал. Используйте беспроводную диагностику Apple. Проверьте конкуренцию со стороны других сетей, измените имя сети, измените канал Wi-Fi — рассмотрите возможность использования диапазона 5 ГГц. Проверьте свои настройки безопасности.
Почему мой Mac продолжает запрашивать пароль WIFI?
Выключите и снова включите Wi-Fi. … Если это не сработает, перезагрузитесь. Если это не сработает, удалите и повторно добавьте службу Wi-Fi в Системные настройки> Сеть.
В чем разница между WPA2 Personal и WPA2 Enterprise?
В чем разница между WPA2 Enterprise и WPA2 Personal? … WPA2 Enterprise использует IEEE 802.1X, который предлагает аутентификацию корпоративного уровня. WPA2 Personal использует предварительные общие ключи (PSK) и предназначен для домашнего использования. Однако WPA2 Enterprise специально разработан для использования в организациях.
Источник
Connecting Apple devices to 802.1X networks
You can securely connect Apple devices to your organization’s 802.1X network.
During the 802.1X negotiation, the RADIUS server presents its certificate to the device supplicant automatically. Be sure that the certificate trust is valid so that the connection is properly validated and the user isn’t presented with a certificate trust error dialog. If the RADIUS server’s certificate isn’t issued from a certification authority (CA) that’s trusted by the operating system by default, trust must also be established in a configuration profile. You may need to include intermediate certificates as well as the root CA certificate.
It’s not necessary to establish a chain of certificate trust in the same profile that contains the 802.1X configuration. For example, an administrator can choose to deploy an institution’s certificate of trust in a standalone profile and can put the 802.1X configuration in a separate profile. This way, modifications to either profile can be managed independently of one another.
To create an 802.1X configuration using configuration profiles, use an MDM solution or Apple Configurator 2 . In addition to creating the parameters for a typical Wi-Fi network, you can create other configurations. For example:
Security type: WPA2 Enterprise or WPA3 Enterprise
For user name–based and password-based EAP types (such as PEAP): The user name or password can be supplied in the profile. If they aren’t supplied, the user is prompted for them.
For certificate identity-based EAP types (such as EAP-TLS): Select the payload that contains the certificate identity for authentication. This can be a PKCS #12 identity certificate (.p12 or .pfx) file in the Certificates payload, a SCEP payload, or an Active Directory Certificate payload (macOS only). By default, iOS and macOS supplicants use the certificate identity common name for the EAP Response Identity it sends to the RADIUS server during 802.1X negotiation.
Shared iPad EAP credentials: Shared iPad uses the same EAP credential for each user.
Trusted certificates: If the RADIUS server’s leaf certificate is supplied in a Certificates payload in the same profile that contains the 802.1X configuration, the administrator can select it here. This configures the client supplicant to connect only to an 802.1X network with a RADIUS server presenting one of the certificates in this list.
Trusted server certificate names: Use this array to configure the supplicant to connect only to RADIUS servers presenting certificates that match these names. This field supports wildcards; for example, *.example.com expects the certificate common names radius1.example.com and radius2.example.com.
802.1X configurations for Mac
You can also use WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Enterprise authentication at the login window of macOS, so that the user logs in to authenticate to the network. The macOS Setup Assistant also supports 802.1X authentication with user name and password credentials using TTLS or PEAP. For more information, see the Apple Support article Use Login Window Mode for 802.1X authentication to a network.
There are two types of 802.1X configurations:
User mode: This mode, the simplest to configure, is used when a user joins the network from the Wi-Fi menu and authenticates when prompted. The user must accept the RADIUS server’s X.509 certificate and trust for the Wi-Fi connection.
System mode: System mode is used for computer authentication. Authentication using system mode occurs before a user logs in to the computer. System mode is commonly configured to provide authentication with the computer’s X.509 certificate (EAP-TLS) issued by a local certificate authority.
System+User mode: A System+User configuration is often part of a one-to-one deployment where the computer is authenticated with its X.509 certificate (EAP-TLS). After the user is logged in to the computer, they can join the Wi-Fi network from the Wi-Fi menu and enter their credentials. User credentials might be a user name and passphrase (EAP-PEAP, EAP-TTLS) or a user certificate (EAP-TLS). After the user has connected to the network, their credentials are stored in the login keychain and used to join the network on future connections.
Login Window mode: This mode is used when the computer is bound to an external directory such as Microsoft Active Directory. When Login Window Mode is configured and a user enters their user name and passphrase at the login window, the user is authenticated to the computer and then to the network using 802.1X authentication.
System mode and Login Window mode require configuration by an MDM solution. Configure the Network payload settings with the desired Wi-Fi network settings, and apply in-scope to a device or device group for System mode.
Источник
This is the second in a series of posts describing the process of joining a corporate wifi network that uses a certificate from a Microsoft certificate authority with a Mac. There are four primary tasks to accomplish this:
- Bind the Mac to Active Directory
- Add the Microsoft CA to the keychain
- Request a Machine certificate from the CA
- Configure the wifi network using the certificate for authentication
Part 1 covered the Active Directory binding. Part 2 will cover the other 3 steps.
Trusting the Certificate Authority
You can request a certificate from a Microsoft CA without actually trusting the CA, however you will have problems trying to use theis certificate for wifi authentication unless the issuer is trusted. There are multiple ways to get the root certificate to trust. If you have a domain joined Windows machine handy then you can go to Start > Run and enter certmgr.msc. Find your corporate root CA under Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates and then right-click and select Export from All Tasks. Note that it will not most likely not be named “Corporate Root CA”, this is just an example. If you don’t know what it is called, look for something with your company’s name in it.
Create another configuration profile to handle the certificate trust. Again, I recommend doing this as a stand-alone profile with a single payload so that it can be updated independently of other settings.
Requesting the AD Certificate
You will need to combine both the AD certificate request payload and the network configuration payload in the same configuration profile. This is the only way you can select the certificate as an authentication option for the network.
Apple has a KB article describing the AD certificate request. The example shown in Apple’s screenshot did not work for me. Whereas Apple’s example simply has a hostname, I had to fill in a complete URL in the format http://pki.kevinbecker.org/certsrv, as shown below. Figuring out the name of the CA also gave me some trouble. Looking at a certificate that had been issued to a Windows machine it would appear that the name of my company’s CA is “MyCompany Corporate Issuing CA”. At least in my case, this is incorrect. I found the correct name using adsiedit.msc as described in this Microsoft KB Article. You will also need to provide the credentials for an account that has rights to request certificates.
Again, in the same profile that has the AD Certificate payload, you will also have a payload to join your wifi network using that certificate. The Username for connection to the network needs to be the computer name followed by a dollar sign. The computer name can be specified in several places in OS X so it’s important to make sure you use the same name specified in the Sharing Preference pane and when binding to AD. In this example, I’m using a payload variable %ComputerName%. A complete list of payload variables can be found in this Apple KB Article. For the Identity Certificate select the AD Certificate name that you used in your AD Certificate payload.
Troubleshooting
Mike Boylan wrote an article at afp548.com covering this process on Mountain Lion. Following his guide, I still had some challenges, which I’ve tried to detail in this article, but his instructions for enabling logging were very helpful. The highlights are duplicated here:
If an error occurs when requesting the AD certificate, the profile will fail to install. To enable logging for the profile installation, and thus the certificate failure, issue the following commands in the terminal: sudo defaults write /Library/Preferences/com.apple.MCXDebug debugOutput -2sudo defaults write /Library/Preferences/com.apple.MCXDebug collateLogs 1
You will need to log out or reboot for the change to take effect. Logging information will show up in /Library/Logs/ManagedClient/ManagedClient.log. which you can easily view with the Console app. To disable debug logging, delete /Library/Preferences/com.apple.MCXDebug.plist.
eapolclient handles the EAP-TLS negotiation when joining a WPA2 Enterprise network. Errors are logged to /var/log/system.log. You can also enable more verbose logging by issuing the following command in the terminal:
sudo defaults write /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.eapolclient LogFlags -int -1
The log(s) will be written to /var/log/eapolclient.[interface].log. To disable the verbose logging, simply change the value to 0.
Источник








